Multivariate discrimination of Buryella species from the Lower Eocene of the Outer Flysch Carpathians, Poland
Full text
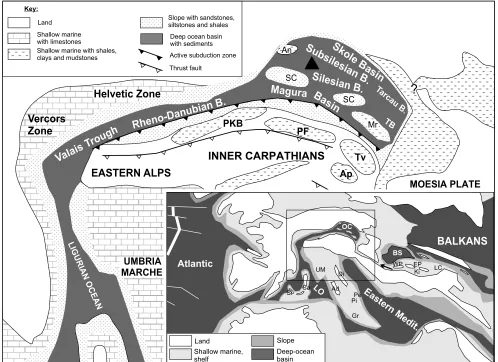
Figure



Related documents
Field experiments were conducted at Ebonyi State University Research Farm during 2009 and 2010 farming seasons to evaluate the effect of intercropping maize with
Intervention effects with respect to ‘ PTA ’ , ‘ INFO ’ , ‘ SAFED ’ , clinical patient outcomes, and health-related quality of life were estimated using general- ised
The NO level increased (p < 0.01) in the liver tissues of rats treated with propolis compared to the L-NAME and L-NAME + propolis groups and was close to the values of
After successfully supporting the development of the wind power technology, an approach is needed to include the owners of wind turbines in the task of realizing other ways, other
Fifty-one IHMs samples were containing 16 dangerous adulterants which are dominated by pain relievers, slimming, aphrodisiac HMs; acetaminophen (ACE), mefenamic acid (MEFA),
A significant decline in the concentrations of renal reduced glutathione in comparison with the control group (C) were observed in the trained and untrained rats intoxicated with
19% serve a county. Fourteen per cent of the centers provide service for adjoining states in addition to the states in which they are located; usually these adjoining states have
To analyse whether moderate voluntary ethanol con- sumption in adult female C57BL/6 mice has any acute toxic and/or cell proliferation effects in the granule cell layer of the
