Silica Nanoparticles for Intracellular Protein Delivery: a Novel Synthesis Approach Using Green Fluorescent Protein
Full text
Figure
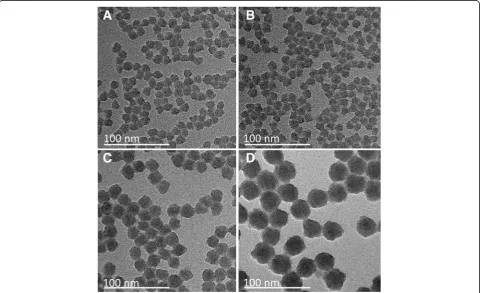
![Table 1 Diameters [nm] of the various particle types derivedfrom TEM and DLS measurements](https://thumb-us.123doks.com/thumbv2/123dok_us/8846885.933399/6.595.57.292.508.684/table-diameters-various-particle-types-derivedfrom-tem-measurements.webp)

![Fig. 5 Influence of temperature (r.t., 60 °C) on the fluorescence offluorescence intensity [%] of the emission maximum at 508 nmGFP-doped particles (CF, ʟ-arginine) and pure GFP](https://thumb-us.123doks.com/thumbv2/123dok_us/8846885.933399/8.595.59.293.501.675/influence-temperature-fluorescence-offluorescence-intensity-emission-particles-arginine.webp)
Related documents
National Conference on Technical Vocational Education, Training and Skills Development: A Roadmap for Empowerment (Dec. 2008): Ministry of Human Resource Development, Department
The aim of this article is to study the role of the Caucasus emirate in shaping security issues in Dagestan with a special focus on its recent structural changes and the
• Follow up with your employer each reporting period to ensure your hours are reported on a regular basis?. • Discuss your progress with
A more recent systematic literature review by Cheney, Schlösser, Nash and Glover (2014), focussed on group interventions used within the UK education system. This
Therefore, many efforts have been devoted to solve most optimal Job Shop Scheduling Problems (JSSP), as most of the researches aimed at minimizing the maximum completion time. JSSP
Table 1 Effect of different growth regulators for callus formation of Hemidesmus indicus. 3.3
’s authentication scheme for GLOMONET, and pre- sented various security pitfalls which include password guessing attack, impersonation attack, replay attack, user anonymity
Simulated scenarios were varied according to the total sample size, the per-exposure risk of infection in control animals, the magnitude and direc- tion of the effect of the
