42
International Journal in Management and Social Science http://ijmr.net.in, Email: irjmss@gmail.comE- BANKING SERVICES OF COMMERCIAL BANKS: A STUDY ON CONSUMERS’ PERSPECTIVE
DR.N.MAHESWARI
Vice-Principal and Assistant Professor in Commerce Computer Application in St.Joseph’s college(Autonomous), Trichirappalli, Tamilnadu.
ABSTRACT
With the expansion of internet usage, e-banking has become one of the most
revolutionized components of today’s economic growth. The purpose of the study is to
identify the views of the customers using e-banking services. The study was carried out to
determine the opinions and problems of customers to enable the banks to understand at
which point the customers cease to be satisfied with the service they are receiving. To
understand the e-banking services provided by the banks , six key service quality
dimensions been taken for analysis are reliability, responsiveness, security, ease use,
accessibility and efficiency key electronic services like ATM, online banking, mobile
banking, credit card and Tele banking. Also the opinions of the respondents regarding the
problems faced by them while dealing with the e-banking services had been considered
for the analysis. The paper identifies the nature of e-banking services provided by the
selected nationalized and private commercial banks in Tiruchirappalli district to evaluate,
analyze and compare the opinions and satisfaction level of customers of e-banking
services provided by the selected nationalized and private commercial banks in
Tiruchirappalli district.
Key words: e-banking, service quality dimensions, nationalized
1. INTRODUCTION
43
International Journal in Management and Social Science http://ijmr.net.in, Email: irjmss@gmail.com details, etc., and to initiate transactions (payment, transfers, requests for services, etc.,) directly with a bank or other financial service provider remotely via a telecommunication network.Electronic banking has become a necessary survival weapon and is fundamentally changing the banking industry worldwide. Today, the click of a mouse offers bank customers services at a much lower cost and also empowers them with unprecedented freedom in choosing vendors for their financial services. No country has a choice whether to implement E-banking or not because of the global and competitive nature of the economy. Banks have to upgrade and constantly think of new innovative customized packages and services to remain competitive.
Emerge of e-banking services
The role of internet has become inevitable to corporate and society. Across the world, government and corporate Are increasingly working towards the better utilization of the internet. The online payment services are extended by the banks for online bill payment, transfer of funds between accounts and cash management services for corporate through debit and credit cards and net banking. Online banking is currently emerging as a new approach in India for providing improved accessibility and expediency to customers.
Expectation of bank customers
Banks are investing a lot of money on web technologies and are therefore expecting numerous benefits on their investments. The intensifying competition on today’s market has forced banks to seek profitable ways to differentiate themselves. The success in their customer centered businesses is to deliver high service quality. Banks have become more aware of customers needs and demands, due the intensifying competition.
2. PROFILE OF THE STUDY AREA
44
International Journal in Management and Social Science http://ijmr.net.in, Email: irjmss@gmail.com3. SCOPE OF THE STUDY
The research is based on the customers’ perception regarding e-banking services. The research discusses the opinion of the customers regarding the e-banking services provided by the banks and the qualities of the e-banking services provided by the banks in the area of reliability, responsiveness, security, easy use, accessibility and efficiency. Also the research analysis the problems faced by the customers while using the e-banking services. The research evaluates the relationship between the activities undertaken through e-banking services by the customers, the qualities of e-banking services and the problems of e-banking services. Debit card, credit card, mobile banking, online banking and Tele-banking are the e-banking services which the customer uses for various modes of services like mobile recharge, payment of telephone bill, payment of electric bill, money transfer, railway ticket booking, air ticket booking, filing of tax return, investments etc., the problems faced by the customers while dealing with e-banking services also taken for analysis of the research.
4. OBJECTIVES
1. To study the nature of e-banking services provided by the selected nationalized and private commercial banks in Tiruchirappalli district.
2. To evaluate, analyze and compare the opinions and satisfaction level of customers of e-banking services provided by the selected nationalized and private commercial banks in Tiruchirappalli district.
3. To understand and compare the problems faced by the customers of the selected nationalized and private commercial banks in Tiruchirappalli district.
METHODOLOGY
The customers who are making use of the electronic banking services provided by the Nationalized and private commercial banks in Trichirappalloi district constitute the universe. Five nationalized and five private banks have been randomly selected for the study. State bank of India(SBI), Indian Bank(IB), Indian Overseas bank(IOB), Canara bank, Bank of India (BOI), ICICI Bank, Lakshmi Vilas Bank(KVB), Karur Vysya bank(KVB), Catholic Cyrian bank(CCB), Federal bank are the commercial banks selected for the study.
45
International Journal in Management and Social Science http://ijmr.net.in, Email: irjmss@gmail.com from 10 banks with the sample size of 500 respondents. A process of cross checking was highly established to ensure the authenticity of the data and the veracity of the interviews with the help of pre-testing and pilot study mechanism. The secondary data and other reviews are collected from the books, journal, newspapers, government publications, annual reports, bulletins and VIP’s address. Analysis of the study is done with the help of the relevant statistical tools like Kruskal-Wallis test, Mann Whitney test, Chi-square test, correlation analysis, one way ANOVA and inter correlation matrix analysis.Limitations
The study is restricted to the customers’ perspectives. Therefore it does not cover any performance appraisal or opinion on e-banking services from banker’s perspectives. The results of the study cannot be substantiated to other areas of the state and country.
5.DATA ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETION
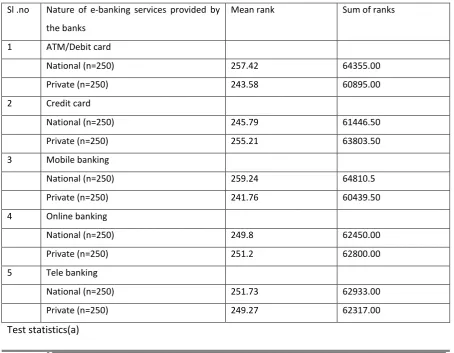
Table 1
Significance between the nationalized banks and private banks of the respondents and their e-banking services
Sl .no Nature of e-banking services provided by
the banks
Mean rank Sum of ranks
1 ATM/Debit card
National (n=250) 257.42 64355.00
Private (n=250) 243.58 60895.00
2 Credit card
National (n=250) 245.79 61446.50
Private (n=250) 255.21 63803.50
3 Mobile banking
National (n=250) 259.24 64810.5
Private (n=250) 241.76 60439.50
4 Online banking
National (n=250) 249.8 62450.00
Private (n=250) 251.2 62800.00
5 Tele banking
National (n=250) 251.73 62933.00
Private (n=250) 249.27 62317.00
46
International Journal in Management and Social Science http://ijmr.net.in, Email: irjmss@gmail.com ATM/Debitcard
Credit card Mobile banking
Online banking
Tele banking
Mann Whitney U
29520.000 30071.500 29064.500 31075.000 30942.000
Wilcoxon W 60895.000 61446.500 60439.500 62450.000 62317.000
Z -1.407 -.741 -1.387 -.110 -.194
Asymp.Sig. (2-tailed)
.159 .459 .165 .912 .846
Source : computed from the primary data
a. Grouping variable : Nationalized/private
Research hypothesis
H1 : There is a significant difference between the nationalized banks and private banks of the
respondents and their e-banking services.
Null hypothesis
H0 : There is a no significant difference between the nationalized banks and private banks of the
respondents and their e-banking services. Statistical test
Mann -Whitney test was used to test the above hypothesis Findings
47
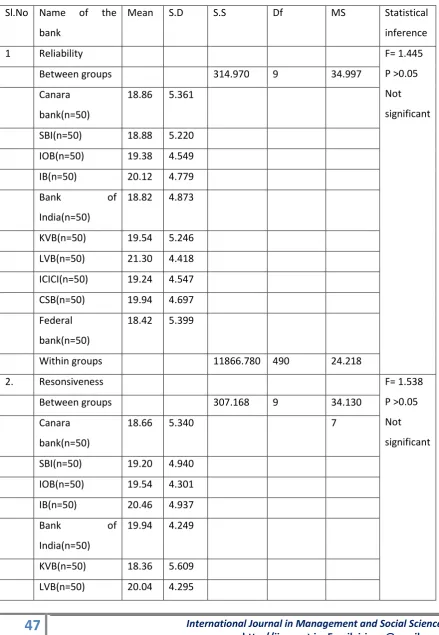
International Journal in Management and Social Science http://ijmr.net.in, Email: irjmss@gmail.comTable 2
Significance between name of the bank of the respondents and their nature of e-banking
services
Sl.No Name of the bank
Mean S.D S.S Df MS Statistical
inference
1 Reliability F= 1.445
P >0.05 Not significant
Between groups 314.970 9 34.997
Canara bank(n=50)
18.86 5.361
SBI(n=50) 18.88 5.220 IOB(n=50) 19.38 4.549
IB(n=50) 20.12 4.779
Bank of
India(n=50)
18.82 4.873
KVB(n=50) 19.54 5.246 LVB(n=50) 21.30 4.418 ICICI(n=50) 19.24 4.547 CSB(n=50) 19.94 4.697 Federal
bank(n=50)
18.42 5.399
Within groups 11866.780 490 24.218
2. Resonsiveness F= 1.538
P >0.05 Not significant
Between groups 307.168 9 34.130
Canara bank(n=50)
18.66 5.340 7
SBI(n=50) 19.20 4.940 IOB(n=50) 19.54 4.301
IB(n=50) 20.46 4.937
Bank of
India(n=50)
19.94 4.249
48
International Journal in Management and Social Science http://ijmr.net.in, Email: irjmss@gmail.com ICICI(n=50) 19.02 3.798CSB(n=50) 18.92 4.877 Federal
bank(n=50)
20.94 4.469
Within groups 10875.800 490 22.196
3 Security F= 0.548
P >0.05 Not significant
Between groups 113.488 9 12.610
Canara bank(n=50)
18.98 5.313
SBI(n=50) 19.60 5.176 IOB(n=50) 18.42 5.047
IB(n=50) 19.54 4.209
Bank of
India(n=50)
19.92 5.230
KVB(n=50) 20.08 4.633 LVB(n=50) 19.32 5.022 ICICI(n=50) 19.92 4.302 CSB(n=50) 19.70 4.566 Federal
bank(n=50)
4.306
Within groups 11277.120 490 24.042
4 Easy use F= 1.117
P >0.05 Not significant
Between groups 9
Canara bank(n=50)
19.52 5.545
SBI(n=50) 20.72 4.021 IOB(n=50) 20.36 5.189
IB(n=50) 19.56 4.807
Bank of
India(n=50)
19.98 5.601
49
International Journal in Management and Social Science http://ijmr.net.in, Email: irjmss@gmail.com CSB(n=50) 21.12 4.663Federal bank(n=50)
20.48 4.577
Within groups 10547.900 490 21.526
5 Accessibility F= 0.372
P >0.05 Not significant
Between groups 71.442 9 7.938
Canara bank(n=50)
20.68 4.316
SBI(n=50) 20.46 4.722 IOB(n=50) 21.18 4.299
IB(n=50) 20.38 4.584
Bank of
India(n=50)
20.68 4.368
KVB(n=50) 20.72 4.824 LVB(n=50) 20.62 4.426 ICICI(n=50) 19.68 5.316 CSB(n=50) 20.12 4.029 Federal
bank(n=50)
20.42 5.171
Within groups 10465.540 490 21.538
6. Efficiency F= 1.328
P >0.05 Not significant
Between groups 232.378 9 25.820
Canara bank(n=50)
20.90 5.556
SBI(n=50) 19.68 5.227 IOB(n=50) 20.78 4.273
IB(n=50) 21.08 4.075
Bank of
India(n=50)
21.30 4.176
50
International Journal in Management and Social Science http://ijmr.net.in, Email: irjmss@gmail.com Federalbank(n=50)
21.44 3.441
Within groups 9530.060 490 19.449
7 Overall
e-banking services
qualities
F= 1.041 P >0.05 Not significant
Between groups 1621.880 9 180.209
Canara bank(n=50)
117.86 13.713
SBI(n=50) 117.92 14.243 IOB(n=50) 120.84 13.633 IB(n=50) 120.02 12.053
Bank of
India(n=50)
120.26 14.540
KVB(n=50) 119.04 13.952 LVB(n=50) 124.42 11.537 ICICI(n=50) 119.98 12.089 CSB(n=50) 121.06 13.332 Federal
bank(n=50)
121.40 12.056
Within groups 84790.920 490 173.043
Source : Primary Data
The table shows the mean calculated on the opinions perceived by the respondents of the different banks regarding the e-banking service qualities of the banks, according to the opinions of the respondents. The above table reveals that there is no significant difference between name of the bank of the respondents and their overall e-banking services qualities [ Reliability = .166>0.05/ Responsiveness = .132 > 0.05/ Security = .839>0.05/ Easy use = .349> 0.05 / Accessibility = .948 > 0.05 / Efficiency = .220 > 0.05/ Overall e-banking services qualities = .406>0.05 ] .
Research hypothesis
H1 : There is a significant difference between name of the bank of the respondents and their
51
International Journal in Management and Social Science http://ijmr.net.in, Email: irjmss@gmail.com Null hypothesisH0 : there is no significant difference between name of the bank of the respondents and their
overall e-banking services qualities . Statistical test
One way ANOVA ‘f test was used to test the above hypothesis
Findings
The table reveals that there is no significant difference between name of the bank of the respondents and their overall e-banking services qualities.
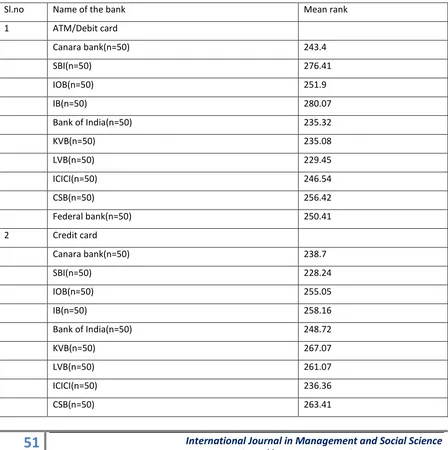
Table 3
Significance between name of the bank of the respondents and their nature of e-banking services
Sl.no Name of the bank Mean rank
1 ATM/Debit card
Canara bank(n=50) 243.4
SBI(n=50) 276.41
IOB(n=50) 251.9
IB(n=50) 280.07
Bank of India(n=50) 235.32
KVB(n=50) 235.08
LVB(n=50) 229.45
ICICI(n=50) 246.54
CSB(n=50) 256.42
Federal bank(n=50) 250.41
2 Credit card
Canara bank(n=50) 238.7
SBI(n=50) 228.24
IOB(n=50) 255.05
IB(n=50) 258.16
Bank of India(n=50) 248.72
KVB(n=50) 267.07
LVB(n=50) 261.07
ICICI(n=50) 236.36
52
International Journal in Management and Social Science http://ijmr.net.in, Email: irjmss@gmail.comFederal bank(n=50) 247.41
3 Mobile banking
Canara bank(n=50) 263.49
SBI(n=50) 256.92
IOB(n=50) 270.79
IB(n=50) 266.99
Bank of India(n=50) 238.02
KVB(n=50) 243.66
LVB(n=50) 217.27
ICICI(n=50) 260.72
CSB(n=50) 237.62
Federal bank(n=50) 249.52
4. Online banking
Canara bank(n=50) 270.50
SBI(n=50) 269.63
IOB(n=50) 234.70
IB(n=50) 210.54
Bank of India(n=50) 263.63
KVB(n=50) 245.1
LVB(n=50) 233.67
ICICI(n=50) 267.51
CSB(n=50) 238.87
Federal bank(n=50) 270.85
5. Tele banking
Canara bank(n=50) 250.04
SBI(n=50) 235.18
IOB(n=50) 288.29
IB(n=50) 250.54
Bank of India(n=50) 234.61
KVB(n=50) 251.53
LVB(n=50) 253.85
ICICI(n=50) 265.78
CSB(n=50) 238.96
Federal bank(n=50) 236.22
53
International Journal in Management and Social Science http://ijmr.net.in, Email: irjmss@gmail.com ATM/Debitcard
Credit card Mobile banking
Online banking
Tele banking
Chi-square 10.583 3.690 6.223 9.781 6.206
Df 9 9 9 9 9
Asymp.Sig .305 .931 .717 .369 .719
Source : Computed from the primary data
a. Kruskal Wallis Test
b. Grouping Variable : name of the respondents’ bank
Research hypothesis
H1 : there is a significant difference between name of bank of the respondents and their nature
of e-banking services
H0 : there is no significant difference between name of bank of the respondents and their nature
of e-banking services Statistical test
Kruskal Wallis test was used to test the above hypothesis Findings
54
International Journal in Management and Social Science http://ijmr.net.in, Email: irjmss@gmail.comTable 4
Significance between name of the bank of the respondents and the various problems faced in
e-banking services
Sl.no Name of the bank and the problems faced by the
respondents
Mean rank
1 Inadequate knowledge about the usage of e-channels
Canara bank(n=50) 272.08
SBI(n=50) 284.32
IOB(n=50) 259.68
IB(n=50) 257.73
Bank of India(n=50) 275.81
KVB(n=50) 227.28
LVB(n=50) 237.16
ICICI(n=50) 244.31
CSB(n=50) 220.95
Federal bank(n=50) 225.68
2 Unsuitable location of ATMs
Canara bank(n=50) 240.02
SBI(n=50) 248.62
IOB(n=50) 270.19
IB(n=50) 230.84
Bank of India(n=50) 270.74
KVB(n=50) 238.21
LVB(n=50) 239.88
ICICI(n=50) 266.60
CSB(n=50) 261.67
Federal bank(n=50) 238.23
3 No of ATMs not sufficient
Canara bank(n=50) 296.94
SBI(n=50) 255.88
IOB(n=50) 206.93
IB(n=50) 238.41
Bank of India(n=50) 241.36
KVB(n=50) 260.08
55
International Journal in Management and Social Science http://ijmr.net.in, Email: irjmss@gmail.comICICI(n=50) 250.30
CSB(n=50) 258.03
Federal bank(n=50) 243.22
4. Poor network
Canara bank(n=50) 266.56
SBI(n=50) 232.36
IOB(n=50) 232.02
IB(n=50) 244.24
Bank of India(n=50) 211.19
KVB(n=50) 270.85
LVB(n=50) 225.03
ICICI(n=50) 30.6.42
CSB(n=50) 251.42
Federal bank(n=50) 264.81
5. Lack of interest from customers
Canara bank(n=50) 282.45
SBI(n=50) 264.05
IOB(n=50) 218.08
IB(n=50) 285.92
Bank of India(n=50) 215.26
KVB(n=50) 241.03
LVB(n=50) 259.41
ICICI(n=50) 216.99
CSB(n=50) 266.93
Federal bank(n=50) 254.88
6. Pass word forgotten
Canara bank(n=50) 255.94
SBI(n=50) 243.74
IOB(n=50) 218.84
IB(n=50) 227.84
Bank of India(n=50) 216.72
KVB(n=50) 258.03
LVB(n=50) 263.72
ICICI(n=50) 270.43
CSB(n=50) 265.65
56
International Journal in Management and Social Science http://ijmr.net.in, Email: irjmss@gmail.com7 Card misplaced
Canara bank(n=50) 235.75
SBI(n=50) 260.74
IOB(n=50) 252.93
IB(n=50) 266.51
Bank of India(n=50) 238.99
KVB(n=50) 244.81
LVB(n=50) 264.03
ICICI(n=50) 256.4
CSB(n=50) 242.74
Federal bank(n=50) 242.10
8 Misuse of card and frauds
Canara bank(n=50) 252.77
SBI(n=50) 239.21
IOB(n=50) 240.22
IB(n=50) 248.14
Bank of India(n=50) 245.22
KVB(n=50) 265.41
LVB(n=50) 242.03
ICICI(n=50) 251.03
CSB(n=50) 272.38
Federal bank(n=50) 248.59
9. Lack of confidence
Canara bank(n=50) 237.67
SBI(n=50) 250.43
IOB(n=50) 231.09
IB(n=50) 226.12
Bank of India(n=50) 269.04
KVB(n=50) 258.44
LVB(n=50) 240.94
ICICI(n=50) 280.94
CSB(n=50) 259.63
Federal bank(n=50) 250.70
10 Technical hurdles of ATMs and smart card
57
International Journal in Management and Social Science http://ijmr.net.in, Email: irjmss@gmail.comSBI(n=50) 229.18
IOB(n=50) 261.66
IB(n=50) 259.36
Bank of India(n=50) 231.10
KVB(n=50) 229.18
LVB(n=50) 239.90
ICICI(n=50) 268.82
CSB(n=50) 232.93
Federal bank(n=50) 247.68
Test statistics (a,b)
Inadequa
te
knowled
ge about
the
usage of
e-channels Unsuitab le location of ATMs
No of
ATMs not sufficie nt Poor netwo rk
Lack of
interest from custome rs Passwo rd forgott en Card misplac ed Misus
e of
card
and
fraud
s
Lack of
confiden ce Technic al hurdles of ATMs and smart card Chi-square
11.226 5.079 10.998 17.775 16.107 11.846 2.794 3.331 8.010 13.980
Df 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9 9
Asymp.S
ig
.261 .827 .276 .038 .065 .222 .972 .950 .533 .123
Source : computed from the primary data a. Kruskal Wallis test
b. grouping variable: name of the bank
Research hypothesis
H1 : there is a significant difference between name of bank of the respondents and various
problems faced in of e-banking services
H0 : there is no significant difference between name of bank of the respondents and various
problems faced in of e-banking services Statistical test
58
International Journal in Management and Social Science http://ijmr.net.in, Email: irjmss@gmail.com FindingsThe table reveals that there is no significant difference between name of the bank of the respondents and various problems faced in e-banking services .
6.FINDINGS OF THE STUDY
The respondents using e banking services been taken equally from all the 10 banks. Out of the total respondents using e-banking services 50 percents of the respondents belong to nationalized banks and 50 percent belong to the private sector banks. Demographic breakdown of the sample presents the frequencies and percentages of the respondents divided according to gender, age, education, occupation and personal monthly income. 75% male respondents in gender wise study were taken. The performance of e-banking channels with respect to the service quality dimensions- the respondents were asked about the latest e-service they have used. It was revealed that most of the customers adopted ATM banking (91.8%) than online banking, mobile banking, credit card and Tele banking. There is highly significant relationship between technical hurdles of ATMs and smart card and poor network, lack of interest from customers, pass word forgotten, card misplaced and lack of confidence.
LITERATURE REVIEW
1. Ankur Gupta (2006), consumer internet banking, with its ability to reach each and every nook and cranny of the world holds great importance for nation like India , where conventional banking services are out of reach for a large proportion for the masses. But to make it a success it requires more than just an adequate internet enabling infrastructure. Ther is a dire need for an adequate legal and regulatory framework to put into place. One of the crucial elements of such a legal and regulatory framework will be data protection provisions. The emphasis of this article is on this aspect of data protection in the electronic banking sector. The article is an attempt to highlight the importance of data protection in internet banking and dwell upon possible legal recourses which may be adopted keeping in mind the current legal framework in India with regards regulation of information technology.
2. Burrett (2008) states online marketing is about ‘carefully targeting users and getting them to interact with you while they’re engaged with the most personal , intimate medium ever invented”. They decide where they want to navigate, what they want to do and which links they want to click.
59
International Journal in Management and Social Science http://ijmr.net.in, Email: irjmss@gmail.com on-line. This paper explores the adoption of internet banking by retail customers in Hong kong. The paper attempts to make sense of internet banking in Hong kong from three angles: [i] the current adoption rate of internet banking ;[ii] the influences of perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, perceived risk and personal innovativeness in information technology and [iii] the potential impacts on the strategic activity of banking organizations operating in the hong kong market.4. Dexiang Wu, Desheng Dash Wu, (2009) online banking has attracted a great deal of attention from various bank stakeholders such as bankers, financial service participants and regulators. The purpose of this paper is to analyse the online banking service performance of gaint US and UK banks. Risk analysis is also conducted.
CONCLUSION
Electronic banking has become a necessary survival weapon and is fundamentally changing the banking industry worldwide. The click of a mouse offers bank customers services at a much lower cost and also empowers them with unprecedented freedom in choosing vendors for their financial service needs. No country today has a choice – whether to implement e-banking or not because of the global and competitive nature of the economy. Customers’ perception of and reaction to the developments of e-banking services are issues of concern to both government and banking industry.
REFERENCES:
1. Ankur gupta, Data Protection in Consumer E-banking, journal of Internet banking and commerce, April 2006, vol.11.no.1
2. Burrett, T.(2008), Market online, B&T Magazine, 58(2682), 44-45.
3. Chi Shing yiu, Kevin Grant, David Edgar, factors affecting the adoption of internet banking in Hongkong- implication for the banking sector, International journal of Information management. Vol 27, issue 5, October 2007, pages 336-351
4. Dexiang Wu, Desheng Dash Wu, (2009) “ performance evaluation and risk analysis of online banking service,” kybemetes, vol.39, issue 5,2009
Websites referred:
1. http://www. Banknetindia.com 2. http://www.rbi.co.in
60
International Journal in Management and Social Science http://ijmr.net.in, Email: irjmss@gmail.com 4. http://www.polaris.co.in5. http://www.acadjournal.com 6. http://www.researchersworld.com 7. http://www. Sbi.com
8. http://www.canarabank.com 9. http://www.kvb@net 10. http://www. Icicibank.com 11. LVBiNET
Books and journals referred 1. Tech quest 2003
2. IBA- Indian year book 2001 3. RBI bulletins
4. E-service journal
5. Journal of internet banking and commerce 6. Journal of financial services marketing 7. Business review
8. Professional banker 9. Internet research