Enhancement of Mobile Computing
Performance for Computational Offloading
Via Device To Device Communication by
Using Ant-Colony Algorithm
Sarala Devi R 1, Bamalakshmi R 2
P.G. Student, Department of Electronics and communication Engineering, GRT IET College, Tiruttani,
Tamil Nadu, India1
Associate Professor, Department of Electronics and communication Engineering, GRT IET College, Tiruttani,
Tamil Nadu, India2
ABSTRACT: Estimation offloading via device-to-device (D2D) communication, or D2D offloading, can improve mobile computing routine by exploit auxiliary computing resources of nearby user diplomacy. The accomplishment of D2D offloading relies on user contribution in mutual service provisioning, which incurs extra costs to users providing the service, thus mandate an incentive mechanism that can compensate for these costs. Although incentive method design has been intensively studied in the narrative, this project considers a much more challenging yet less investigated problem in which selfish users are also facing interdependent security risks, such as infectious propinquity-based attacks. Security cost is significantly different in nature from conventional service provisioning costs such as energy consumption because security risks often depend on the collective behaviour of all users. Finally optimized value is obtained by Ant-colony Algorithm.
KEYWORDS:Device-Device Communication, Mobile computing, Computational Offloading.
I. INTRODUCTION
Device-to-device (D2D) communication that enables direct statement sandwiched between nearby mobiles is a stimulating and pioneering feature of next-age bracket cellular network. It will smooth the progress of the interoperability between critical public safety networks and omnipresent business-related networks based on e.g. LTE. We should analyse and design such hybrid networks consisting of both cellular and ad hoc links WNCG Profs. Jeffrey Andrews and Constantine, in association with lead researchers are operational to enlarge novel models on behalf of such hybrid cellular systems and to use them for network presentation appraisal and design. This study concerned close group endeavour with and remarkable technical inputs from the Head of NSN North America Radio Systems, Amitava Ghosh, and Principal Engineer Mazin Al-Shalash from WNCG Industrial Affiliate Huawei. Their occupation has impacted 3GPP standards hand-outs from NSN and Huawei on unambiguous D2D technology in LTE.
The researchers bring into being that to take full advantage of the total throughput; D2D links with more traffic to broadcast should be more aggressive in their spectrum access, even with the interference this generate to the rest of the network. In a seriously loaded network, the total throughput remuneration from offloading local traffic to D2D mode, as D2D communication only requires “1” hop while relaying via a BS requires “2” hops. They supplementary investigate the optimal resource sliding doors between D2D and cellular networks, and found that the choice of dedicated and shared approaches depends on the D2D traffic and the resource partition in dedicated networks. The enthusiastic approach may achieve larger throughput in a network with many unthinking D2D links and optimal store partition.
II. RELATEDWORK
Data and computation offloading is used to address the inherent problems in mobile computing by using resource providers other than the mobile device itself to host the execution of mobile applications. This paper focuses on D2D offloading which uses nearby mobile devices as resource providers via D2D communication. In general, computation offloading is concerned with what/when/how to offload a user’s workload from its device to other resource providers (see and references therein). The problem studied in this paper is not contingent on any specific offloading technology. Rather, we design incentives in the presence of interdependent security risks and hence, our approach can be used in conjunction with any existing offloading technology. D2D offloading benefits from the fact that mobile users in close proximity can establish direct wireless communication link over the licensed spectrum (in band) or unlicensed spectrum (out band) while bypassing the cellular infrastructure such as the BSs. This new communication paradigm can significantly improve the system throughput, energy efficiency, fairness and overall QoS performance. In practice, D2D communication has been implemented in industry products such as Qualcomm FlashLinQ and standardized by 3GPP. Enabled by D2D communication, D2D offloading can further alleviate computation burdens from the edge computing infrastructure.
III. METHODOLOGY
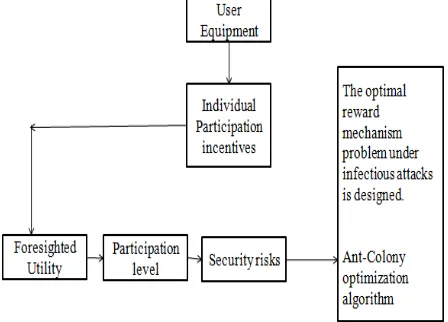
USER EQUIPMENT
In the Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) and 3GPP Long Term Evolution (LTE), user equipment (UE) is any gadget exercise straight by an customer to correspond. It know how towards be a hand-held mobile, a laptop computer capable to through a mobile broadband adapter, or several other apparatus It connects to the station Node/eNodeB as specific in the ETSI 125/136-series and 3GPP 25/progression of qualifications. It generally corresponds just before the mobile station (MS) in GSM systems. The radio boundary involving the UE and the Node B is called Uu. UE handle the subsequent responsibilities towards the core network.
INDIVIDUAL PARTICIPATION INCENTIVES
A reasonable in sequence practice principle, it is the principle that an personality must have the precise a) to attain from a information controller, or else, authentication of whether or not the data controller has data relating to him; b) to have data describing to him communicated to him within a reasonable time; at a charge, if any, that is not unwarranted; in a realistic manner, and in a form that is voluntarily understandable to him; c) to be given reasons if a request made under subparagraphs (a) and (b) is denied, and to be able to challenge such denial; and d) to brave data unfolding to him and, if the challenge is victorious, to have the data erased, rectify, completed or amend.
FORESIGHTED UTILITY
PARTICIPATION LEVEL
The operator assigns computation tasks to UEs according to their chosen participation levels whenever D2D offloading is needed. Due to UE mobility and the randomness in the task arrival, we model the D2D offloading request arrival assigned to UE i as a Poisson process.
SECURITY RISK:
Security of data transmission is an important concern in cloud based application processing. Security and privacy are two crucial concepts that need to be maintained during the offloading process. These concepts can be addressed from different angles: (1) Mobile device, (2) cloud data centers, and (3) during data transmission over the network. Besides all the technologies, there is a great increase in the variety of sophisticated attacks on mobile phones which are the main targets for attackers. Regarding the security in the cloud data centers, threats are basically related to the transmission of data between the different nodes over the network. Thus, high levels of security are expected by both the mobile clients and the cloud providers. In the current frameworks binary transfer of the application code at runtime is continually subjected to security threats. Despite the available solutions, strong measures and a secure environment are required for the three entities of MCC model.
Fig 1 Proposed block diagram
ANT-COLONY ALGORITHM
Ant colony optimization (ACO) is a population-based metaheuristic so as to preserve be worn to find estimated solutions to easier said than done optimization problems. In ACO, a set of software agents called artificial ants search for good solutions to a given optimization problem. To apply ACO, the optimization difficulty is distorted into the problem of pronouncement the best path on a weighted graph. The non-natural ants (hereafter ants) incrementally put together solutions by affecting on the graph. The solution construction process is stochastic and is biased by a pheromone model, that is, a set of parameters associated with graph components (either nodes or edges) whose values are modified at runtime by the ants.
IV. RESULTS
Value obtained in the user equipment:
Fig 2 Four cells with much cellular equipment
To simplify our analysis, assume that the minimum contract duration is small enough so that UEs can effectively modify their contracts at any time. In this section, we can use many user devices to interconnect with each other. At every stage the signal gets more efficient signal. The consequent protocols are transmitted obviously via a Node B, that is, Node B does not modify use or comprehend the information. The UE is a mechanism which initiates all the calls along with it is the terminal device in a network.
Graph for foresighted utility:
Fig 3 Foresighted utility
normal state until the next time (say t0 +t) when it interacts with a compromised UE, the attack by the compromised UE is successful and the UE has not been compromised during [t0, t0+t). This is a random process (where t is the random variable).
Graph for System Compromise state:
Fig 4 System Compromise state
The figure show the operator’s utility and the fraction of compromised UEs as functions of the reward r0 and the effective infection rate, which are in accordance with our analysis. Thus, high levels of security are expected by both the mobile clients and the cloud providers. In the current frameworks binary transfer of the application code at runtime is continually subjected to security threats. Despite the available solutions, strong measures and a secure environment are required for the three entities of MCC model. The security threat is advancing in a quick manner more than we can keep up with it. Security techniques need to enhance and progress constantly to meet new changes and new offered services.
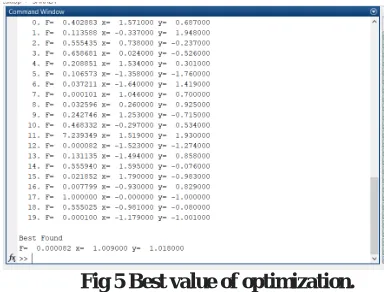
Optimization value:
Fig 5 Best value of optimization.
V. CONCLUSION
We analysed the foremost important but much less studied incentive mechanism design problem in dynamic networks where users’ incentives and security risks they face are intricately coupled. We adopted a dynamic non-cooperative game theoretic approach to recognize how user collaboration incentives are influenced by interdependent security risks such as the communicable attack risks, and how the attack risks originate, broadcast, persist and turn off depending on users’ strategic choices. This understanding authorized us to create security-aware incentive mechanisms that are able to fight and moderate attacks in D2D offloading systems. Our study controls the classic epidemic models, but on the other hand, it corresponds to a significant disappearance from these models since users are intentionally choosing their actions pretty than dutifully following few approved rules.
REFERENCES
[1] H. T. Dinh, C. Lee, D. Niyato, and P. Wang, “A survey of mobilecloud computing: architecture, applications, and approaches,” Wirelesscommunications and mobile computing, vol. 13, no. 18, pp. 1587–1611,2013.
[2] Y. Mao, C. You, J. Zhang, K. Huang, and K. B. Letaief, “A surveyon mobile edge computing: The communication perspective,” IEEECommunications Surveys Tutorials, vol. 19, no. 4, pp. 2322–2358, 2017.
[3] E. E. Marinelli, “Hyrax: cloud computing on mobile devices usingmapreduce,” DTIC Document, Tech. Rep., 2009.
[4] C. Shi, V. Lakafosis, M. H. Ammar, and E. W. Zegura, “Serendipity:enabling remote computing among intermittently connected mobile devices,”in ACM international symposium on Mobile Ad Hoc Networkingand Computing. ACM, 2012, pp. 145–154.
[5] D. Chatzopoulos, M. Ahmadi, S. Kosta, and P. Hui, “Have you askedyour neighbors? a hidden market approach for device-to-device offloading,”in IEEE International Symposium on A World of Wireless,Mobile& Multimedia Networks (WoWMoM). IEEE, 2016, pp.1–9.
[6] M. Haus, M. Waqas, A. Y. Ding, Y. Li, S. Tarkoma, and J. Ott, “Securityand privacy in device-to-device (d2d) communication: A review,” IEEECommunications Surveys Tutorials, vol. 19, no. 2, pp. 1054–1079, 2017.