A Study on 5G Technology
Tejas Bhor, Pinak Kalola
Department of M.C.A, University of Mumbai, A.S.M. Instistute of Management and Computer Studies (IMCOST), Thane(W), Mumbai, India
ABSTRACT: Mobile and wireless networks have made tremendous growth in the last fifteen years. Nowadays several mobile phones have additionally a WLAN adapter. One may suppose that close to presently several mobile phones canhave WiMAX adapter too, besides their 3G, 2G, WLAN, Bluetooth etc. adapters. Today 3G mobile systems square measure on the ground providing scientific discipline property for period and non-real-time services. On the other aspect, there are several wireless technologies that have tested to be necessary, with the most important ones being 802.11 Wireless native space Networks (WLAN) and 802.16 Wireless Metropolitan space Networks (WMAN), as well as ad-hoc Wireless Personal Area Network (WPAN) and wireless networks for digital TV and broadcast. The main contribution of this paper is definition of 5G (Fifth Generation) mobile network concept, which is seen as user-centric construct instead of operator-centric as in 3G. In the proposed construct the mobile user is on the highest of all. The 5G terminals will have package outlined radios and modulation theme as well as new error-control schemes may be downloaded from the net on the run. The development is seen towards the user terminals as a spotlight of the 5G mobile networks. Each network can be accountable for handling user-mobility, while the terminal can create the final alternative among completely different wireless/mobile access network suppliers for a given service. The paper also proposes intelligent net phone construct wherever the mobile phone will select the simplest affiliations by chosen constraints and dynamically amendment them throughout one end-to-end connection. The proposal in paper is prime shift within the mobile networking philosophy compared to existing 3G and near-soon 4G mobile technologies, and this concept is termed here- the 5G.
KEYWORDS: WiMAX,WPAN, PLMN, OWA, EGPRS,TACS, AMPS, IMTS
I. INTRODUCTION
phone will select the simplest affiliations by chosen constraints and dynamically amendment them throughout one end-to-end connection.
II. EVOLUTIONFROM1GTO5G
Cell phones are used millions and billions of users worldwide. How several folks understand the technology behind cell phones that's used for our communication? I even have additionally intrigued regarding the sort of technology
employed in my phone. What are 1G, 2G, 3G and 4G technologies?
1G, 2G, 3G & 4G ("G" stands for "Generation") are the generations of wireless telecommunication property. 1G (Time Division Multiple Access and Frequency Division Multiple Access ) was the initial wireless telecom network system. It's out-dated now. The analog “brick phones” and “bag phones” are underneath 1G technology. Cell phones era began with 1G.
The next era, 2G has taken its place of 1G. Cell phones received their first major upgrade once they went from 1G to 2G. This leap effectively took cell phones from analog to digital. 2G and 2.5G were versions of the GSM and CDMA connections. And GSM is still the foremost popular technology, but with no net. Fortunately, GPRS, an extra service, is provided over GSM for the purpose of internet access. GPRS has been developed and thus, EGPRS was created. It's more secure and quicker than GPRS.Then 3G came, the new Wireless CDMA technology. It is the primary wireless telecom technology that gives broadband-speed net affiliation on mobile phones. It has been specially made for the demand of net on sensible phones. Further development junction rectifier to the creation of three.5G, which provides blazing quick net affiliation on phones, up to the speed of 7.2 MBPS. A smart phone may be connected to a computer to share its net affiliation {and three and three}3G and 3.5G are ideal for this. But, as this WCDMA technology is not available altogether regions, its not as popular as GSM nonetheless. Before making the major leap from 2G to 3G wireless networks, the lesser-known 2.5G was an interim normal that bridged the gap. Following 2.5G, 3G ushered in faster data-transmission speeds thus you may use your telephone in additional data-demanding ways in which. This has meant streaming video (i.e. movie trailers and television), audio and much a lot of. Cell phone companies these days square measure disbursement plenty of cash to complete to you the importance of their 3G network. The above systems and radio interfaces square measure based mostly on kindred unfold spectrum radio transmission technology. While the GSM EDGE normal ("2.9G"), DECT cordless phones and Mobile WiMAX standards formally additionally fulfill the IMT-2000 needs and square measure approved as 3G standards by ITU, these are generally not branded 3G, and are based mostly on fully completely different technologies. 4G, which is additionally referred to as “beyond 3G” or “fourth-generation” telephone technology, refers to the entirely new evolution. Developers are currently going for 4G, which can give net up to the speed of one GBPS! It aforementioned to be able to overcome the issues of weak network strength and will give a way wider network, making certain that the users get high-speed proper anytime anyplace. No doubt, 4G will open new doors of revolutionary net technologies, but for currently, 3G and 3.5G are the best. 4G will enable for speeds of up to 100Mbps. 4G promises voice, data and high-quality transmission in period kind all the time and anyplace.
II.1.1GWIRELESSSYSTEM
First Generation wireless technology (1G) is the original analog (An analog or analogue signal could be any continuous signal that the time varied feature (variable) of the signal is an illustration of another time varied quantity), voice-only cellular telephone normal, developed in the 1980s. The main difference between 2 succeeding mobile phone systems,
1G and 2G, is that the radio signals that 1G networks use are analog, while 2G networks square measure digital. .
Push to Talk (PTT).
Keys:
1. Developed in 1980s and completed in early 1990’s
2. 1G was old analog system and supported the first generation of analog cell phones speed up to two.4kbps 3. Advance mobile phone system (AMPS) was first launched by the America and could be a 1G mobile system 4. Allows users to create voice calls in one country
FIG.1G Mobile Phone
II.2..2G WIRELESS SYSTEM
2G (or 2-G) is short for second-generation wireless telephone technology. Second generation 2G cellular telecom networks were commercially launched on the GSM normal in Suomi by Radiolinja (now half of ELISA Oyj) in 1991. 2G network allows for abundant bigger penetration intensity. 2G technologies enabled the various transportable networks to produce the services like text messages, picture messages and MMS (multi media messages). 2G technology is more economical. 2G technology holds sufficient security for each the sender and the receiver. All text messages are digitally encrypted. This digital encryption permits for the transfer of information in such some way that solely the supposed receiver will receive and browse it.
Keys:
1.Fielded within the late 1980s and finished in the late Nineteen Nineties 2.Planned for voice transmission with digital signal and the hurries up to64kbps 3.2G was the digital handsets that we square measure used these days
4.2G network allows for abundant bigger penetration intensity.
FIG. 2G Mobile Phone
II.3.2.5G WIRELESS SYSTEM
2.5G is a stepping stone between 2G and 3G cellular wireless technologies. The term "second and a half generation" is used to explain 2G-systems that have enforced a packet switched domain additionally to the circuit switched domain. It does not essentially give quicker services as a result of bundling of timeslots is employed for circuit switched information services (HSCSD) furthermore.
The first major step within the evolution of GSM networks to 3G occurred with the introduction of General Packet Radio Service (GPRS). CDMA2000 networks similarly evolved through the introduction of 1xRTT. So the cellular services combined with increased information transmission capabilities became referred to as '2.5G.' GPRS could give information rates from fifty six Kbit/s up to a hundred and fifteen Kbit/s. It can be used for services like Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) access, Multimedia electronic messaging Service (MMS), and for Internet communication services such as email and World Wide net access. GPRS data transfer is generally charged per MB of traffic transferred, while information communication via ancient circuit switch is beaked per minute of affiliation time, independent of whether or not the user truly is utilizing the capability or is in AN idle state.1xRTT supports bi-directional (up and downlink) peak data rates up to 153.6 kbps, delivering an average user information output of 80-100 kbps in business networks. It can additionally be used for WAP, SMS & MMS services,
as well as Internet access.
Keys:
1. In between 2 G and 3G there is another generation called 2.5G 2. 2.5G represents handsets with data capabilities over GPRS 3. But this had not brought out any new revolution
II.4.3G WIRELESS SYSTEM
International Mobile Telecommunications-2000 (IMT--2000), better best-known as 3G or third Generation, is a generation of standards for mobile phones and mobile telecommunications services fulfilling specifications by the International Telecommunication Union. The use of 3G technology is additionally able to transmit packet switch datawith efficiency at higher and enlarged information measure. 3G mobile technologies proffers more advanced services to mobile users. The spectral efficiency of 3G technology is higher than 2G technologies. Spectral efficiency is the measure of rate of knowledge transfer over any communication system. 3G is also referred to as IMT-2000
.1. Transmission speeds from 125kbps to 2Mbps
2. In 2005, 3G is ready to measure up to its performance in laptop networking (WCDMA, WLAN and Bluetooth) and mobile devices space (cell phone and GPS)
3. Data square measure sent through technology referred to as packet switch 4. Voice calls are understood victimization circuit switch
5. Access to Global Roaming 6. Clarity in voice calls
7. Fast Communication, Internet, Mobile T.V, Video Conferencing, Video Calls, Multi Media Messaging Service (MMS), 3D gaming, Multi-Gaming etc are additionally offered with 3G phones
FIG.3G Mobile Phone
II.5.4G WIRELESS SYSTEM
348kbits once moving or traveling. ITU sell various frequency rates in order to create use of broadband technologies. Network authentication has won the trust of users, because the user will bank on its network as a reliable supply of transferring information.3G technology is much versatile, because it is able to support the five major radio technologies. These radio technologies operate under CDMA, TDMA and FDMA.CDMA holds for IMT-DS (direct spread), IMT-MC (multi carrier). TDMA accounts for IMT-TC (time code), IMT-SC (single carrier). FDMA has only one radio interface referred to as IMT-FC or frequency code. Third generation technology is really reasonable attributable to the agreement of trade. This agreement took place so as to extend its adoption by the users. 3G (Third Generation Technology) system is compatible to work with the 2G technologies. 3G (Third Generation Technology) technologies holds the vision that they should be expandable on demand. The aim of the 3G (Third Generation Technology) is to allow for a lot of coverage and growth with minimum investment. The bandwidth and location info offered to 3G devices offers rise to applications not antecedently offered to transportable users. Some of the applications are:
1. Mobile TV – a provider redirects a TV channel on to the subscriber's phone wherever it may be watched. 2. Video on demand – a provider sends a show to the subscriber's phone.
3. Video conferencing – subscribers can see as well as see one another.
4. Tele-medicine – a medical provider monitors or provides recommendation to the probably isolated subscriber. 5. Location-based services – a provider sends localized weather or traffic conditions to the phone, or the phone allows the subscriber to realize close businesses or friends
6. mobile ultra-broadband (gigabit speed) access and multi-carrier transmission. 7. Mobile WiMAX (Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access)
Keys:
1. 4G is a conceptual framework and a discussion purpose to deal with future wants of a high speed wireless network 2. It offer each cellular and broadband transmission services everyplace
3. Expected to emerged around 2010 – 2015
4. 4G should be in a position to provided terribly swish world roaming ubiquitously with lower price
II.6. 5G WIRELESS SYSTEM
5G (5th generation mobile networks or 5th generation wireless systems) is a name employed in some analysis papers and comes to denote subsequent major part of mobile telecommunications standards on the far side the approaching 4G standards (expected to be finalized between roughly 2011 and 2013). Currently, 5G is not a term officially used for any specific specification or in any legal document nonetheless created public by telecommunication corporations or standardization bodies like 3GPP, WiMAX Forum or ITU-R. New 3GPP standard releases on the far side 4G and LTE Advanced square measure in progress, but not thought of as new mobile generations. The implementation of standards under a 5G umbrella would seemingly be around the year of 2020.
Keys:
1. 5G is a completed wireless communication with almost no limitation; somehow folks referred to as it REAL wireless world
2. Additional options such as Multi-Media Newspapers, also to watch T.V programs with the clarity as to that of an HD T.V.
3. We will send information abundant quicker that that of the previous generations
4. 5G will bring nearly good real world wireless or referred to as “WWWW: World Wide Wireless net 5. Real wireless world with no more limitation with access and zone problems.
6. Wearable devices with AI capabilities.
7. Internet protocol version vi (IPv6), where a visiting care-of mobile scientific discipline address is allotted according to location and connected network.
8. One unified global normal.
9. Pervasive networks providing ubiquitous computing: The user will at the same time be connected to many wireless access technologies and seamlessly move between them (See Media freelance relinquishment or vertical relinquishment, IEEE 802.21, also expected to be provided by future 4G releases). These access technologies can be a two.5G, 3G, 4G or 5G mobile networks, Wi-Fi, PAN or any other future access technology. In 5G, the concept might be any developed into multiple synchronic information transfer methods. 10. Cognitive radio technology, also best-known as smart-radio: permitting completely different radio technologies to share an equivalent spectrum with efficiency by adaptively finding unused spectrum and adapting the transmission theme to the wants of the technologies presently sharing the spectrum. This dynamic radio resource management is achieved in a distributed fashion, and relies on package outlined radio. See also the IEEE 802.22normal for Wireless Regional space Networks.
11. High altitude stratospheric platform station (HAPS) systems.
I.5G WIRELESS SYSTEM
5G Technology stands for 5th Generation Mobile technology. 5G technology has changed the means to use cell phones within very high bandwidth. User never experienced ever before such a high value technology. Nowadays
mobile users have much awareness of the cell phone (mobile) technology. The 5G technologies include all type of
advanced features which makes 5G technology most powerful and in huge demand in near future.
The gigantic array of innovative technology being built into new cell phones is stunning. 5G technologies which are on hand held phone offering more power and features than at least 1000 lunar modules. A user can also hook their 5G technology cell phone with their Laptop to get broadband internet access. 5G technology including camera, MP3 recording, video player, large phone memory, dialling speed, audio player and much more you never imagine. For children rocking fun Bluetooth technology and Pico nets has become in market.
WHAT 5G TECHNOLOGY OFFERS?
future because it can handle best technologies and offer priceless handset to their customers. May be in coming days 5G technology takes over the world market. 5G Technologies have an extraordinary capability to support Software and
Consultancy. The Router and switch technology used in 5G network providing high connectivity. The 5G technology
distributes internet access to nodes within the building and can be deployed with union of wired or wireless network connections. The current trend of 5G technology has a glowing future.
IV.CONCEPTS FOR 5G MOBILE NETWORKS
The 5G terminals will have package outlined radios and modulation schemes as well as new error-control schemes which will be downloaded from the net. The development is seen towards the user terminals as a spotlight of the 5G mobile networks. The vertical handovers should be avoided, because they square measure not possible in a very case once there square measure several technologies and plenty of operators and repair suppliers. In 5G, each network can be accountable for handling user-mobility, while the terminal can create the final alternative among completely different wireless/mobile access network suppliers for a given service. Such choice can be supported open intelligent middleware within the transportable.
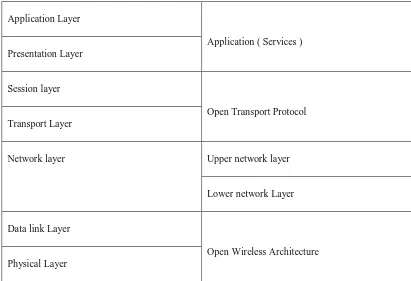
TABLE. OSI Layers in the 5G Mobile Terminal Design
Application Layer
Application ( Services ) Presentation Layer
Session layer
Open Transport Protocol Transport Layer
Network layer Upper network layer
Lower network Layer
Data link Layer
Open Wireless Architecture Physical Layer
PHYSICAL LAYER
Physical and Medium Access Control layers i.e. OSI layer 1 and OSI layer two, define the wireless technology. For these two layers the 5G mobile networks is seemingly to be supported Open Wireless design.
NETWORK LAYER
FIG.5G Mobile Terminal Network Layer
The 5G mobile phone shall maintain virtual multi-wireless network environment. For this purpose there should be separation of network layer into 2 sub-layers in 5G mobiles (Fig.) i.e.: Lower network layer (for each interface) and higher network layer (for the mobile terminal). This is attributable to the initial design of the net, where all the routing is based mostly on scientific discipline addresses that ought to vary in every scientific discipline network world wide. The middleware between the Upper and Lower network layers (Fig. 3) shall maintain address translation from Upper network address (IPv6) to completely different Lower network scientific discipline addresses (IPv4 or IPv6), and vice versa.
OPEN TRANSPORT PROTOCOL (OTA) LAYER
The mobile and wireless networks differ from wired networks concerning the transport layer. In all TCP versions the belief is that lost segments square measure attributable to network congestion, while in wireless networks losses might occur due to higher bit error magnitude relation within the radio interface. Therefore, TCP modifications and adaptation square measure planned for the mobile and wireless networks, which transmit the lost or broken communications protocol segments over the wireless link solely. For 5G mobile terminals will be appropriate to possess transport layer that's attainable to be downloaded and put in. Such mobiles shall have the possibility to transfer (e.g., TCP, RTP etc. or new transport protocol) version which is targeted to a specific wireless technology put in at the bottom stations. This is called here Open Transport Protocol - OTP.
APPLICATION LAYER
Regarding the applications, the ultimate request from the 5G mobile terminal is to produce intelligent QoS management over type of networks. Today, in mobile phones the users manually select the wireless interface for specific net service while not having the risk to use QoShistory to pick the simplest wireless affiliation for a given service. The 5G phone shall provide risk for service quality testing and storage of measure info in databases in the mobile terminal. The QoS parameters, such as delay, jitter, losses, bandwidth, reliability, will be hold on in a very information within the 5G transportable with aim to be employed by intelligent algorithms running within the mobile terminal as system processes, which at the finish shall give the simplest wireless affiliation upon needed QoS and private price constraints.
V.FEATURES
1. 5G technology offer high resolution for crazy cell phone user and bi- directional giant information measure shaping. 2. The advanced billing interfaces of 5G technology makes it a lot of engaging and effective.
3. 5G technology also providing subscriber supervising tools for quick action. 4. The high quality services of 5G technology supported Policy to avoid error.
5. 5G technology is providing large broadcasting of information in Gigabit that supporting nearly sixty five,000 connections.
8. Through remote management offered by 5G technology a user can get higher and quick resolution. 9. The remote diagnostics additionally a nice feature of 5G technology.
10. The 5G technology is providing up to 25 Mbps property speed. 11. The 5G technology also support virtual non-public network.
12. The new 5G technology will take all delivery service out of business prospect 13. The uploading and downloading speed of 5G technology touching the peak.
14. The 5G technology network offering increased and offered property simply regarding the globe
VI.CONCLUSION
In this paper we've proposed 5G transportable construct, which is the main contribution of the paper. The 5G mobile phone is intended as an open platform on completely different layers, from physical layer up to the application. Currently, the ongoing work is on the modules that shall give the simplest QoS and lowest price for a given service victimization one or quite one wireless technology at an equivalent time from the 5G transportable.
A new revolution of 5G technology is near to begin because 5G technology planning to provide powerful completion to traditional laptop and laptops whose marketplace worth are going to be established. There are heaps of enhancements from 1G, 2G, 3G, and 4G to 5G in the world of telecommunications. The new coming 5G technology is offered within the market in reasonable rates, high peak future and much reliableness than its preceding technologies.
REFERENCES
[1] Toni Janevski, “AAA System for PLMN-WLAN Internetworking”, Journal of Communications and Networks (JCN), pp.192-206, Volume 7,Number 2, June 2005.
[2] Janise McNair, ang Zhu, “Vertical Handoffs in Fourth-Generation Multinetwork Environments”, IEEE Wireless Communications, June2004. [3] Toni Janevski, “Traffic Analysis and Design of Wireless IP Networks”, Artech House Inc., Boston, USA, 400 p., May 2003.
[4] Suk Yu Hui, Kai Hau Yeung, “Challenges in the Migration to 4G Mobile Systems”, IEEE Communications Magazine, December 2003. [5] Bria, F. Gessler, O. Queseth, R. Stridth, M. Unbehaun, J.Wu, J.Zendler, “4-th Generation Wireless Infrastructures: Scenarios and Research
Challenges”, IEEE Personal Communications, Vol. 8,