EFFECTIVENESS OF PLANNED TEACHING PROGRAMME ON
KNOWLEDGE REGARDING ATTENTION DEFICIT HYPER
ACTIVITY DISORDER (ADHD) IN CHILDREN’S AMONG PRIMARY
SCHOOL TEACHERS
*Ashish Gautam
*Assistant Professor Psychiatric Nursing Department College of Nursing, Bharati Vidyapeeth
Deemed University, Sangli, Maharashtra, India.
ABSTRACT
One in five children has a clinically significant psychiatric disorder
that should be treated. A major portion of the hyperactive child’s
problem related to difficulties in performing age appropriate task.
Hyperactive children are highly distractible and have extremely limited
attention span. Early identification and treatment of those children is
critical in order to reduce risk for psychiatric disorders, reaching into
their adult lives. Teachers are often the first one who to recognize or
suspect psychiatric disorder in children, that is because lack of
attention in school of child and in some cases disrupts the rest of class
and because the teacher are with children day-in and day-out. Thus the
researcher felt that there is a need to asses an “Effectiveness of planned
teaching programme on knowledge regarding Attention Deficit Hyper
Activity Disorder (ADHD) in children’s among Primary School Teachers.”. Results &
finding of the study are when the sample were taken for study the samples had less
knowledge about ADHD. The planned teaching on knowledge regarding ADHD was found
to be effective in increasing the knowledge in primary school teacher’s. the samples had
significant gain in knowledge after the planned teaching programme.
KEYWORDS: Attention Deficit Hyper Activity Disorder (ADHD), Primary School
Teachers.
Volume 6, Issue 7, 1402-1406. Research Article ISSN 2277– 7105
*Corresponding Author
Ashish Gautam
Assistant Professor
Psychiatric Nursing
Department College of
Nursing, Bharati Vidyapeeth
Deemed University, Sangli,
Maharashtra, India. Article Received on 15 May 2017,
Revised on 05 June 2017, Accepted on 25 June 2017
INTRODUCTION
Hyperactive children have difficulty forming satisfactory interpersonal relationship. They
demonstrate behavior that inhibits acceptable social interactions. They are descriptive and
intrusive in a group endeavors. They have difficulty complying with social norms. Some
children with ADHD are very aggressive or oppositional, where as other exhibit more
aggressive and immature behavior. Low frustration tolerance and out burn of temper are not
common. Children with ADHD have boundless energy, exhibiting excessive level of activity,
restlessness and fidgeting. Since teachers work with many different children, they also come
to know how control, so they noticed something outside of room, they may speak with school
psychologist or contact the parent about their concerns. The teacher can tell what they have
noticed. ADHD diagnosis is based on observation of child behavior, the teacher and past
teacher will play a key role in process through professional who make the diagnosis usually a
specially trained teacher to create their observation of child. Thus the researcher found the
importance to assess on knowledge regarding Attention Deficit Hyper Activity Disorder
(ADHD) in children’s among Primary School Teachers.”.
TITLE -“A study to evaluate the effectiveness of planned teaching programme on
knowledge regarding Attention Deficit Hyper Activity Disorder (ADHD) in children’s among
primary school teachers in selected schools of Sangli-Miraj-Kupwad Corporation area.”.
OBJECTIVIES
1) To assess the existing knowledge regarding Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
(ADHD) in children’s among primary school teachers.
2) To evaluate the effectiveness of planned teaching programme on knowledge regarding
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in children’s among primary school
teachers
3) To find out association between pre test knowledge score with the selected demographic
variables (i.e. age, education, experience).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
DESCRIPTION OF TOOL
Tools are divided into two parts:
1) Demographic data
2) The structured Questionnaire Assessment on knowledge of ADHD.
POPULATION OF THE STUDY: Primary School Teachers.
SAMPLE SIZE- The sample size selected for the study is 50 primary school teachers.
SAMPLING TECHNIQUE: In the present study the non probability purposive sampling
technique.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Organization of research data divides into three sections
1) Description of sample according to demographic characteristics-
Majority of the primary school teachers 32% are between the age group of 40-50 years &
30% are between age group of 21-30 years & 28% are between age group 31-40 years while
10% of teachers are between the age group of 51-60 years. In education level of primary
school, 46% had education up to graduate level while 34% were educated up to post
graduation level. 20% of primary school teachers had education teaching diploma in
education. In pervious knowledge of ADHD 84% teachers don’t have, remaining 16% have
pervious information on knowledge of ADHD.
2) Analysis of data related to comparison between knowledge scores of primary school
teachers before & after plan teaching program.
Table -1 N=50=100%
Test Mean SD T DF P
PRE-TEST 9.140 3.381
8.272 49 0.00
Figure -1 N=50=100%
Comparison of level of knowledge score in frequency & percentage of primary school
[image:4.595.133.466.353.558.2]teachers in pre & post test.
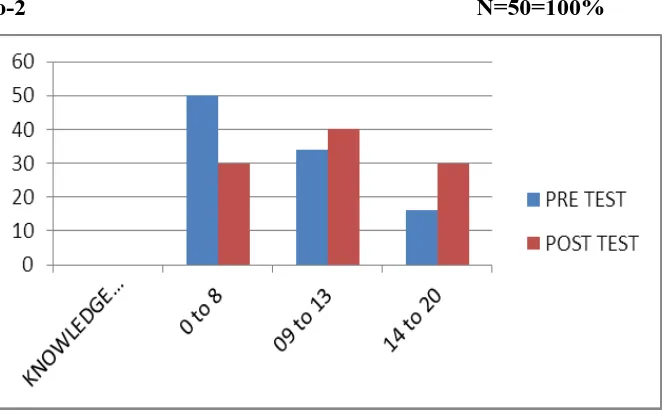
FIGURE No-2 N=50=100%
FIGURE No-2 presents that the majority of 50% of primary school teachers in pre-test
of study were having poor knowledge score (0-8), 34% of primary school teachers in
pretest of study group were having average knowledge score(9-13) while 16% of
primary school teachers in pretest of study group having good knowledge (14-20%).
Whereas as in posttest majority 40% primary school teacher have average knowledge score
3) Analysis of data to find association between pre test knowledge score with selected
demographic variable’s per the finding, it shows that there is no correlation in pre test
knowledge score with selected demographic variable Like age, educational status,
pervious knowledge regarding ADHD.
CONCLUSIONS
The following conclusions were made from the following finding of the study. when the
sample were taken for study the samples had less knowledge about ADHD. The planned
teaching on knowledge regarding ADHD was found to be effective in increasing the
knowledge in primary school teachers. the samples had significant gain in knowledge after
the planned teaching programme. The planned teaching on knowledge of ADHD was found
to be effective in enhancing to become aware of the significant ADHD & the role of primary
school teachers in ADHD treatment.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
My sincere thanks to administrator of primary school for valuable data for my research work
I specially thank the participants of this study, without whose co-operation it would have
been impossible to conduct the study.
REFERENCES
1. The impact of an ADHD training program on teacher knowledge ERIN
E.CUNNINGHAM State University.
2. South African Journal of Education, copyright 2010 EASA volume -30 457-473.
3. Gautam A. A comparative study to assess cognitive impairment of old people residing in
old age home versus with those living the family of Pune. Research & Reviews: Journal of
Health Professional. 2016; 6(1).
4. ABELL, & SEWELL. J (1999). stress and burnout it rural & urban primary teachers,
journal of educational research page no-: 92: 287-293.
5. Gautam A. A study to assess the effectiveness of planned teaching programme on
knowledge regarding temper tantrums among mothers of toddlers in selected areas of
Sangli, Miraj & amp; Kupwad Corporation area. Journal of Nursing Science and Practice.