ACCELERATOR 6.3
ASTERISK LINES INTEGRATION GUIDE
© 2004 - 2014 Tango Networks, Inc.
This software is protected by copyright law and international treaties, and is the confidential and proprietary information of Tango Networks, Inc. Unauthorized reproduction, use, or distribution of this software, or any portion of it, may result in severe civil and criminal penalties, and will be prosecuted to the maximum extent possible under the law. The software described in this document is furnished under license agreement and may only be used in accordance with the terms of the agreement. Tango Networks and Abrazo are trademarks of Tango Networks, Inc. All other trademarks used herein are the property of their respective owners and are used for identification purposes only.
© 2004 - 2014 Tango Networks, Inc.
Tango Networks, Abrazo and E=fmc2 are trademarks or registered trademarks of Tango
Networks, Inc. All other trademarks or service marks are the property of their respective owners. Specifications and features are subject to change without notice.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION ... 4
SUPPORTED VERSIONS ... 4
INTERCONNECTION VIA SIPTRUNKS,SIPLINES, AND WEB SERVICES ... 4
ACCELERATOR INTEGRATION PROCESS ... 5
ASTERISK TRIXBOX PROVISIONING ... 5
Ensure Multiple Devices per User Setting is Enabled ... 5
Login to Trixbox ... 6
Add an Asterisk User ... 7
Add a SIP Device – User’s Desk Phone ... 9
Add a User’s Desk Phone ... 9
Add a Second Device to Sim Ring the Mobile ...12
Add Trunk ...13
Pilot DN Configuration ...15
Voicemail Configuration ...19
ACCELERATOR PROVISIONING ...20
Mobile UC Enabled Accelerator ...20
Voice Network: PBX/Trunk Dial Plan...20
Voice Network: Extension Ranges ...21
Voice Network: Carrier Gateways ...21
Voice Network : Voice Mail...22
Subscriber Dial Plan/Subscriber ...22
FEATURE INTERACTIONS ... 23
ACCELERATOR PBXLEVEL 1INTEGRATION ...23
ACCELERATOR PBXLEVEL 2INTEGRATION ...26
ACCELERATOR PBXLEVEL 3INTEGRATION ...26
ACRONYMS ... 27
FIGURES
Figure 1 Asterisk Trixbox Administration Web Interface ... 6Figure 2 Initial Asterisk Status Screen ... 6
Figure 3 Select PBX Settings ... 6
Figure 4 Users Menu ... 7
Figure 5 Add Users Menu ... 7
Figure 6 Add Asterisk User ... 8
Figure 7 Select Devices ... 9
Figure 8 Select Generic SIP Device ... 9
Figure 9 Add SIP Device ...10
Figure 10 Select SIP Device ...10
Figure 11 Modify Device ...11
Figure 12 Second Device for Sim Ringing Mobile ...12
Figure 13 Trunks Menu ...13
Figure 14 Add SIP Trunk Option ...13
Figure 15 Add SIP Trunk ...14
Figure 16 Tools Menu – Custom Destinations ...15
Figure 17 Add Custom Destination for Accelerator ...15
Figure 18 Config File Editor ...16
Figure 19 Config File Editor Configuration List ...16
Figure 20 Edit Extensions Configuration File ...16
Figure 21 Re-Read Configs ...17
Figure 22 Inbound Routes ...17
Figure 23 Add Incoming Route ...18
Figure 24 Feature Codes for Voice Mail settings ...19
Introduction
Tango extends enterprise PBX functionality to mobile devices allowing end users to be more productive and accessible when out of the office. Tango integrates mobile devices with existing PBXs so that the PBX sees the mobile device as simply another desk phone. This allows the existing PBX feature set to be applied consistently across both devices. Mobile specific functionality is then layered on top.
Supported Versions
This document addresses the way that Tango integrates with the Asterisk Lines 1.4 PBX. Trixbox CE version 2.6.2.2 is used as the provisioning GUI interface to the Asterisk Lines PBX. This document is intended for users with a thorough understanding of the Asterisk 1.4 PBX and Trixbox CE 2.6.2.2.
Interconnection via SIP Trunks, SIP Lines, and Web Services
The Accelerator uses a combination of SIP lines and trunks to integrate with the Asterisk Lines 1.4 PBX. SIP lines are used so that Tango-controlled mobile devices appear as standard SIP phones and therefore benefit from the
common set of PBX services offered to such devices. SIP trunks are used in certain mobile termination scenarios when call control must be transferred to Asterisk for feature processing prior to the call being routed to the mobile and any associated desk phone.
Accelerator Integration Process
Asterisk Trixbox Provisioning
The following summary outlines the Asterisk 1.4 provisioning requirements: 1. Ensure multiple devices per user setting is enabled – The
Accelerator-enabled Asterisk user must be able to assign at least two devices to their user profile.
2. Login to Trixbox – Provisioning on the Asterisk Lines 1.4 PBX is accomplished using the Trixbox interface.
3. Add an Asterisk user
4. Add SIP Device – User’s Desk Phone
5. Add SIP Device – Second device needed to simultaneously ring the user’s mobile phone when the enterprise number is called.
6. Define a SIP trunk on the Asterisk Lines PBX to route between Asterisk and the Accelerator.
7. Define a pilot number to route calls from the wireless carrier into the enterprise Asterisk 1.4 PBX.
8. Voice mail configuration.
Ensure Multiple Devices per User Setting is Enabled
The Asterisk Lines 1.4 PBX must be enabled to allow multiple devices to be assigned for a single user. One device is defined as the desk phone and the second device is defined to simring the mobile phone when the enterprise number is called.
1. ssh into the Asterisk Lines PBX as root. Edit the file /etc/amportal.conf Find and modify the following line:
AMPEXTENSIONS=deviceanduser
The setting must reflect deviceanduser so that a single user can have multiple devices assigned to them. Save and close the file. Log out of the ssh session.
Login to Trixbox
2. Access the Trixbox administration web interface by using the URL
http://ip-address/maint in a browser window, where ip-address is
the IP address of the Trixbox server. Log in with the appropriate credentials. The first screen of the interface is displayed.
Figure 1 Asterisk Trixbox Administration Web Interface
Select switch to switch to administrator mode and login. The following screen is displayed.
Figure 2 Initial Asterisk Status Screen
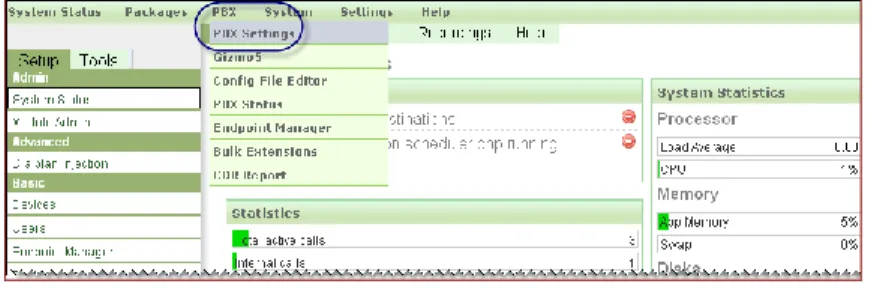
Once logged in navigate to PBX ->PBX Settings.
Add an Asterisk User
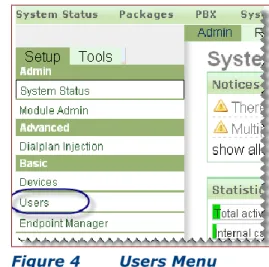
3. In the left navigation panel, select Users.
Figure 4 Users Menu
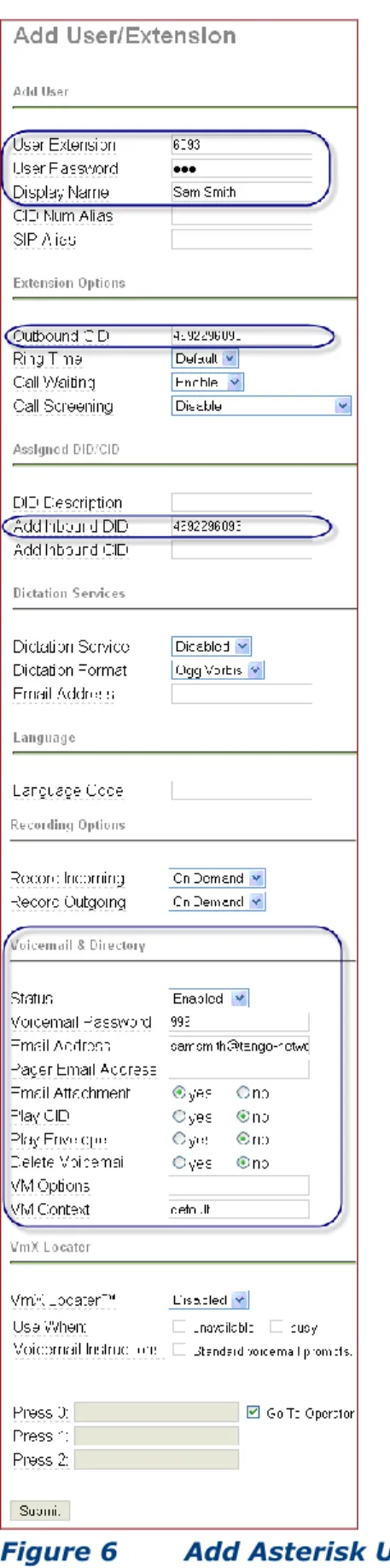
The screen changes to the Add User/Extension page. Find the right most panel and click Add User.
Complete and submit the user information. Provide the Outbound CID, Add
Inbound DID and Enable the Voicemail section.
Add a SIP Device – User’s Desk Phone
Add a User’s Desk Phone
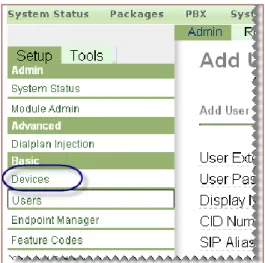
4. From the left navigate panel,select Devices.
Figure 7 Select Devices
The Add Device screen will be displayed. From the Device pull down
menu, select Generic SIP Device. Click Submit.
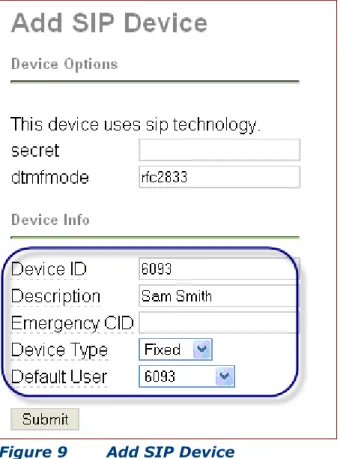
The Add SIP Device screen will be displayed. Enter the Device ID,
the Description, and select the Default User for the device. Click on
Submit.
Figure 9 Add SIP Device
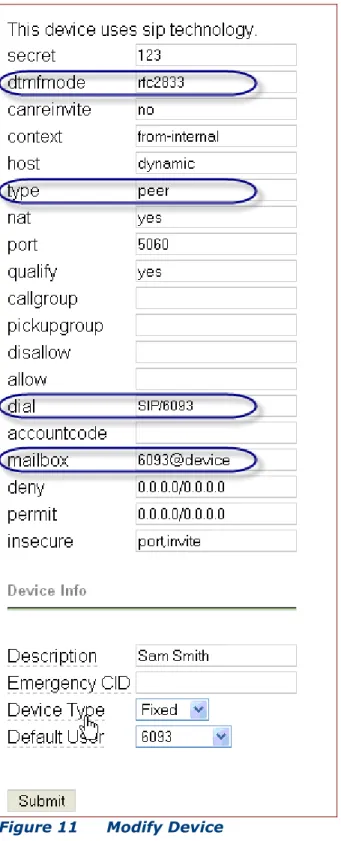
Modify the SIP Device by selecting it from the Device list. The following screen will be shown.
The modify device screen will be displayed. The field dtmfmode must
be rfc2833. The type field must be peer. The dial field must have
the extension number (e.g. 6093). Also include the mailbox information as extension number@device (e.g. 6093@device).
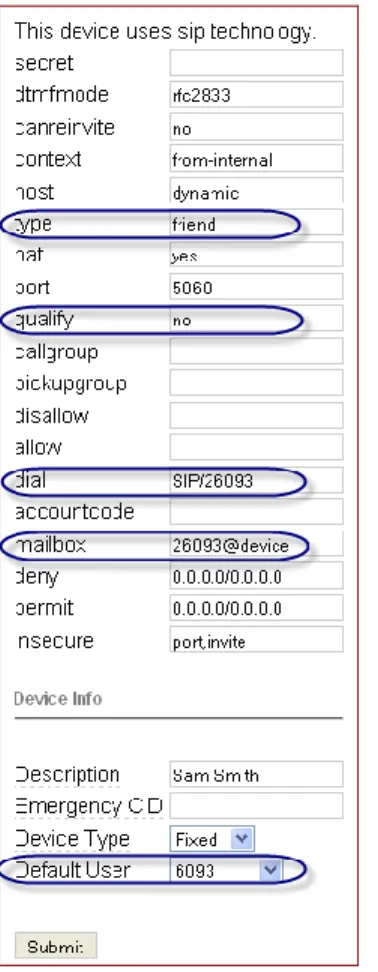
Add a Second Device to Sim Ring the Mobile
The second device is used to simultaneously ring the mobile phone when the enterprise number is called.
5. Repeat the instructions described in step 4 above. The only differences are:
Device ID – Give the new device a unique Device ID. In our
example, we used Sam’s desk phone extension and prefixed it with the number ‘2’.
Make note of this extension as it will be needed for the SIP Address when provisioning the Accelerator subscriber.
default User – Select the user’s desk phone extension.
After submitting the initial extension information, modify the device and ensure the following:
type – set as friend
qualify – set as no
dial – set with new extension such as SIP/26093
mailbox – set with new extension such as 26093@device
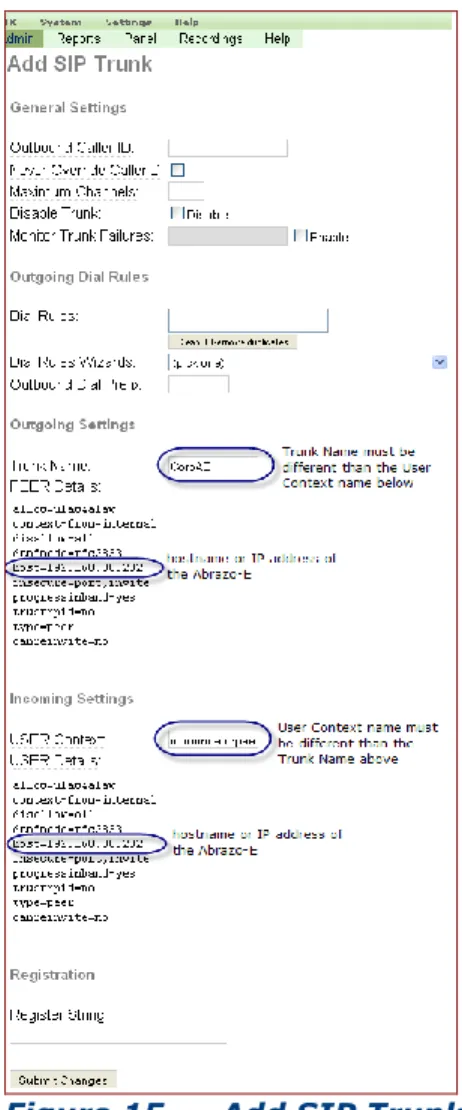
Add Trunk
6. In the left most menu, click the Trunks topic.
Figure 13 Trunks Menu
Click the Add SIP Trunk option in the middle of the page. The screen changes to the Add SIP Trunk page.
Submit the following SIP trunk field information. The Outgoing
Trunk Name must match the Accelerator’s Asterisk Lines PBX Domain
name. Here we defined the outgoing trunk name as CorpAE which is the same name we used on the Accelerator for the Asterisk Lines PBX Domain field. (Refer to page Error! Bookmark not defined. – Voice Network: PBX, Add PBX bullet.)
Peer Details and User Details should reflect the values shown in
Figure 15. Supply a User Context name that is different than the trunk name.
All other fields can be left at their default values:
Pilot DN Configuration
If calls to Pilot DNs will be routed to the Accelerator via the Asterisk PBX then the appropriate Route configuration must be created within Asterisk. If Pilot DNs are routed directly to the Accelerator from the wireless operator network then no Route configuration must be specified within Asterisk.
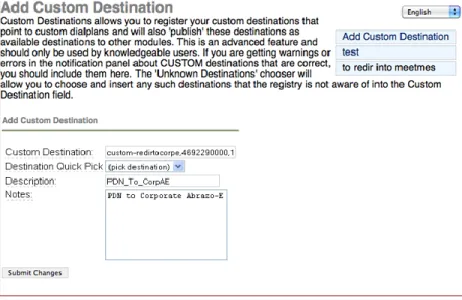
7. On the left panel, select Tools. From the Tools menu, select Custom
Destinations.
Figure 16 Tools Menu – Custom Destinations
Add a Custom Destination for the Accelerator Server. The PDN entered here must be a PSTN routable number within the DID block assigned to the enterprise. In our example, we named the destination
as custom-redirtocorpe and defined the PDN as 4692290000.
From the PBX pull-down menu, select Config File Editor.
Figure 18 Config File Editor
From the list of configuration files, select extensions_custom.conf.
Figure 19 Config File Editor Configuration List
Enter the definition of the Custom Destination defined earlier. Click
on Update to submit the changes.
On the extensions_custom.conf menu, select Re-Read Configs to apply the changes to the Asterisk Lines PBX.
Figure 21 Re-Read Configs
Return to the PBX Settings as described in Figure 3 on page 6. Under the Setup Menu on the left panel, select Inbound Routes.
Add an Incoming Route which will define the PDN to be associated with the appropriate Accelerator.
Submit the following field information:
– DID Number – The PDN for the Accelerator.
– Custom Destinations – The destination defined for the
Accelerator.
Voicemail Configuration
Voicemail for each Asterisk user should have been enabled during user creation. See Figure 6 on page 8 for user voice mail settings.
Voice mail provisioning on the Accelerator will require mailbox deposit and retrieval numbers. These numbers are found in the Feature Codes menu on the Trixbox as described below.
8. The Asterisk voicemail number can be found at the following location on the Trixbox. Find the Feature Codes menu topic.
Figure 24 Feature Codes for Voice Mail settings
Scroll to the bottom of the Feature Codes page and locate the My
Voicemail entry. The number provisioned here reflects both the voice
mail deposit and retrieval numbers entered on the Accelerator for Voicemail provisioning.
Accelerator Provisioning
Note: This document assumes that the Accelerator has already been provisioned with:
- Enterprise information
- Wireless carrier information. The Carrier(s) should be enabled for Mobile UC and/or PSTN Access.
Mobile UC Enabled Accelerator
The section discusses the integration process for a Mobile UC enabled Accelerator.
The steps below describe the unique configuration areas needed to integrate the Asterisk PBX with the Accelerator solution. Refer to the Accelerator Provisioning Guide for a comprehensive explanation of Accelerator provisioning.
The integration process includes the following steps:
Voice Network: PBX/Trunk Dial Plan
1. Add Trunk Dial Plan (required) – There are no unique configuration
items for Trunk Dial Plans and the Asterisk PBX. Refer to the Accelerator Provisioning Guide, Voice Networks, PBXs,Add Trunk Dial Plan section.
2. Add PBX (required) – he PBX Domain field must match the Asterisk SIP
trunk name described in Figure 15 on page 14. All other field values are not unique to the integration. Refer to the Accelerator Provisioning Guide,
Voice Networks, PBXs, Add New PBX section.
If your enterprise intends to use the Route via Enterprise mobile policy by routing Pilot DNs through the PBX to the Accelerator, go ahead and
provision the Pilot DNs on the PBX’s main page under the Pilot Numbers section. Note that the Pilots here must be E.164 routable. The pilot DN defined in the Pilot DN Configuration section starting on page 15 is used here. In our example, the PDN is 4692290000.
Also, if your enterprise intends to use the Call Move service, go ahead and provision the Call Service Pilots on the PBX’s main page under the Call
Service Pilot Numbers section. Note that the Pilots here do not have to
be E.164 routable. Note that the Call Move feature access code can be found on the Accelerator provisioning page at: Services ->Feature
Add Trunk Groups/Trunk (required) –o Host Address, Port and
Transport Type
should match the IPAddress of the Asterisk PBX with a port value of 5060.
If the hostname is entered, the Accelerator queries the DNS server for the associated DNS SRV records. This allows for redundancy and/or load balancing based on the DNS SRV records if the customer has deployed multiple Asterisk servers. Refer to the Accelerator
Provisioning Guide, Voice Networks, PBXs (Add/Modify), Add Trunk Groups/Trunks section.
o Trunk Group Request URI parameters are not used by the Asterisk PBX and therefore do not need to be provisioned.
Add Line Groups/Line(required) – At least one line group with anassociated line must be provisioned for the Asterisk Lines PBX on the Accelerator. The configuration is not unique to this integration.
o Host Address, Port and Transport Type should match the IP
Address of the Accelerator PBX with a port value of 5060.
If the hostname is entered, the Accelerator queries the DNS server for the associated DNS SRV records. This allows for redundancy and/or load balancing based on the DNS SRV records if the customer has deployed multiple Asterisk servers. Accelerator Provisioning Guide,
Voice Networks, PBXs (Add/Modify), Add Line Groups/Line section.
o Line Group Request URI parameters are not used by the Asterisk PBX
and therefore do not need to be provisioned.
Add Least Cost Routing(optional) - No unique configuration items for
Least Cost Routing. Refer to the Accelerator Provisioning Guide, Voice Networks, PBX, Least Cost Routes, Add Least Cost Routes section.
Voice Network: Extension Ranges
3. Add Extension Ranges (required) – No unique configuration items for
adding an Extension Range. Refer to the Accelerator Provisioning Guide,
Voice Networks, Extension Ranges, Add New Extension Ranges section.
Voice Network: Carrier Gateways
4. Carrier Gateways (required if your enterprise routes calls between the
wireless carrier and the Accelerator) – If your enterprise intends to use an SBC or Carrier Gateway between the carrier and the enterprise, then add a Carrier Gateway. Be sure to supply the Outbound Domain as required by the add Carrier Gateway page.
If you are using Pilot numbers to route calls from the wireless carrier to the Accelerator using the Carrier Gateway, provision the Pilot Numbers on the Carrier Gateway’s main page. Depending on your configuration, the Pilot numbers here may need to be E.164 routable.
Add Trunk Groups/Trunk (required if using a Carrier Gateway) –o Host Address, Port and
Transport Type
should match the value ofIf the hostname is entered, the Accelerator queries the DNS server for the associated DNS SRV records. This allows for redundancy and/or load balancing based on the DNS SRV records if the customer has deployed multiple Asterisk servers. Refer to the Accelerator
Provisioning Guide, Voice Networks, Carrier Gateway (Add/Modify), Add Trunk Groups/Trunks section.
Trunk Group Request URI parameters are normally not required by most SIP endpoints, however, consult your carrier’s instructions.
Add Least Cost Routing(optional) - No unique configuration items forLeast Cost Routing. Refer to the Accelerator Provisioning Guide, Voice Networks, Carrier Gateway, Least Cost Routes, Add Least Cost Routes
section.
Voice Network : Voice Mail
5. Add Voice Mail for the Asterisk Lines PBX in the Accelerator. Select PBX as the Voice Mail Server Type. The values for the voice mail deposit and retrieval numbers are discussed starting on page 19 of this document. Refer to the Accelerator Provisioning Guide, Voice Networks, Voice Mail Servers, Add Voice Mail Server section.
Subscriber Dial Plan/Subscriber
6. Add Subscriber Dial Plan (required) - No unique configuration items for
adding Subscriber Dial Plans. Refer to the Accelerator Provisioning Guide, Subscribers, Add Subscriber Dial Plan section.
7. Add Subscribers(required) - One item to note when provisioning
subscribers:
– SIP Address – The SIP Address is associated with the Asterisk
user’s second device as discussed starting on page 12. In our example, the second device is 26903.
The domain name of the SIP Address must match the Asterisk outgoing trunk name and the Accelerator PBX Domain field. In our example, the Accelerator subscriber record’s SIP Address field looks like this:
26903@corpae
– Enable the Home PBX Provides Orig Svcs setting. – Select the Voice Mail Server created in step 8 above.
– Provide the Asterisk user’s desk extension number for the Voice
Mailbox Number. In our example we used 6903.
Feature Interactions
The intent of Tango is to seamlessly add a mobile component to all of the services that the Asterisk Lines PBX provides to the end user. The Accelerator is integrated with PBXs at three levels of integration. The Asterisk Lines PBX is integrated at Level 2 integration. This section explains the PBX features that have been integrated with this Accelerator release.
Accelerator PBX Level 1 Integration
Integration Level 1 provides the subscriber basic services that are commonly used. The following features are considered Level 1:
Abbreviated Dialing - Allows extension dialing or internal dialing from
the desktop phone. The Accelerator allows the user to dial these same abbreviated numbers from the mobile phone.
Ad Hoc Conferencing (Internal to PBX) - Allows an Accelerator
subscriber to initiate a reservation-less conference from a mobile phone using the conference resources of the PBX.
Ad Hoc Conferencing using (External to PBX) - Allows an Accelerator
subscriber to initiate a reservation-less conference from a mobile phone using external media server located in the enterprise.
Call Forward All (Desk) - Allows users to forward all calls to another
destination including those calls to the mobile number. This feature is activated via the desk phone.
Call Forward Activation on Mobile - - Allows users to forward all calls
to another destination. Users enter a feature access code on their mobile phone to activate or deactivate call forwarding.
Call Forward Busy (Desk) - Allows users to forward calls (including
those to their mobile number) to another destination when their device is busy. Users activate or deactivate the Call Forward Busy capability with a Call Forward Busy feature button from their desk phone
Call Forward Busy Activation on the Mobile - Allows users to forward
calls to another destination when their device is busy. Users activate or deactivate the Call Forward Busy capability with a feature access code from their mobile phone.
Call Forward No Answer (Desk) - Allows users to forward calls
(including calls to their mobile number) to another destination when their device is not answered. Users activate or deactivate the Call Forward No Answer capability with a Call Forward No Answer feature button from their desk phone
Call Forward No Answer Activation on Mobile - Allows users to
forward calls to another destination when their device is not answered. Users activate or deactivate the Call Forward No Answer capability with a feature access code from their mobile phone.
Call Hold and Retrieve (Mobile) – Lets users temporarily disconnect from a call, use the telephone for another call, and then return to the original call. The Accelerator supports this capability in concert with the wireless network.
Call Line Identification (CLID) – Provides the user information about
the calling party. The Accelerator supports calling line identification when it is the called party. The Accelerator also supports ensuring that the enterprise identity of the caller is preserved when a call is initiated from the mobile phone. In this case although the call is made from a mobile, the calling line ID will be that of the Accelerator user's desktop phone. The enterprise main number may also optionally be used in place of a
subscriber’s DID for off-net calling.
Call Transfer – Lets users move a currently established call from their
mobile phone to another destination. This is implemented by the user entering a mid-call feature code followed by the transfer to number. There are two types of call transfers that are supported by this functionality:
o Blind Call Transfer – Call is transferred without interaction between
the user who initiated the transfer and the transfer destination.
o Consultative Call Transfer - Call is transferred allowing interaction
between the user who initiated the transfer and the transfer destination.
Call Waiting and Retrieve - Provides users with an audible alert in the
voice stream that a new incoming call is waiting. The user can retrieve the call from the desk phone. The Accelerator supports call waiting in concert with the wireless network. Call Waiting tones are provided by the mobile phone when an incoming call is waiting, and waiting calls can be retrieved from the mobile phone.
Direct Inward Dialing - Allows the desk phone to be directly accessed
from the PSTN. The Accelerator supports enterprise Direct Inward Dialing.
Direct Outward Dialing - Allows users inside an enterprise to dial
directly to an external number. The Accelerator supports the mobile device dialing directly to an external number.
Directory Dial - Lets users select numbers to dial from a corporate or
personal directory. The Accelerator supports using a personal directory on the phone and handles the translations of those digits into on-net network numbers if appropriate. In addition, The Accelerator support a corporate directory look up capability for access to the corporate address book.
Flexible Dialing Support - The Accelerator has a flexible dialing plan
enabling PBX services to be provided to mobile users.
Intelligent Call Delivery - Ensures that both the desk phone and mobile
phone ring when the dialed number is an Accelerator subscriber.
Least Cost Routing – For mobile originations and terminations, the
Accelerator ensures that the least cost route is used. This results in the enterprise voice network being used to route the call as much as possible, reducing PSTN interconnect costs, and other voice costs such as roaming.
Meet-Me Conference - Allows users to set up a dial-in conference of up
to six parties. The mobile user can participate in the meet-me conference by dialing the conference bridge.
Multiple Calls per Line – Allows multiple calls to be delivered to a single number and have the incoming call information displayed to the user. The Accelerator supports this feature on the mobile phone based on the ability to support call waiting for mobile phone devices. Mobile devices typically show a maximum of two lines per mobile phone.
PBX Do Not Disturb (Desk) – Allows users to activate or deactivate the
Do Not Disturb capability by pressing a button or a softkey from their desk phone. When active, Do Not Disturb will not ring the mobile or desk
phone.
PBX Do Not Disturb (Mobile) - Allows users to activate or deactivate
the Do Not Disturb capability by entering a feature access code from their mobile phone. When active, Do Not Disturb will not ring the mobile phone however the desk phone will continue to ring.
Single Number Services - A single phone number that a subscriber
publishes to communicate with others. When this single number is dialed, the subscriber’s enterprise desktop phone as well as mobile phone will ring.
Voice Mail Waiting Indication - Provides a visible indication on the
mobile phone that there is a message waiting in the voice mail system. The Accelerator supports supplying a Message Waiting indication on the mobile phone that indicates that there are voice mail messages in the enterprise voice mail system.
Table 1 Accelerator PBX Level 1 Integration
Feature Support Comments
Abbreviated Dialing Yes Ad Hoc Conferencing (Internal to PBX) Yes
Ad Hoc Conferencing (External to PBX) Yes
Uses an external IP Media 2000 conference server. Refer to the Accelerator Provisioning Guide, Voice Networks, Conference Servers section.
Call Forward All (Desk) Yes Call Forward All Activation from Mobile Yes Call Forward Busy (Desk) Yes Call Forward Busy Activation from Mobile Yes Call Forward No Answer (Desk) Yes Call Forward No Answer Activation from Mobile Yes Call Hold and Retrieve (Mobile) Yes Call Line Identification (CLID) Yes Call Transfer – Blind Yes Call Transfer – Consultative Yes Call Waiting and Retrieve Yes Direct Inward Dialing Yes Direct Outward Dialing Yes
Directory Dial Yes
Flexible Dialing Support Yes Intelligent Call Delivery Yes Least Cost Routing Yes Meet-Me Conference Yes Multiple Calls per Line Yes PBX Do Not Disturb (Desk) Yes PBX Do Not Disturb (Mobile) Yes
Accelerator PBX Level 2 Integration
Integration Level 2 provides the subscriber more advanced features than more commonly used basic features. The following features are considered Level 2 integration targets:
Call Accounting Codes - To support the mobile office environment, client
billing must be supported when the user is away from his/her desktop phone and using a mobile phone. For example, law offices, accounting firms, consulting firms and other organizations benefit from tracking the length of a call for a client. Client billing is achieved by having the user enter a code to specify that the call relates to a specific client matter or account. The code, which is often referred to as a client matter code (CMC) or call accounting code, can be assigned to customers, students, or other populations for call accounting and billing purposes. Call accounting codes are used by enterprise to manage call accounting.
Call Coverage/Hunt Groups - Allows a group of extensions to be set up
to handle multiple calls to a single telephone number. For each call to the number, the PBX hunts for an available extension in the hunt group and connects the call to that extension. The Accelerator can be defined as one of the extensions.
Call Line Identification Restriction (CLIR) (Mobile) - Allows the user
to restrict their calling line information from being displayed to the called number. The Accelerator supports restriction of calling line identification from mobile phones. Enterprise identity will be replaced; however
restriction code will be preserved.
Call Pull (Desk->Mobile Call Move) - Allows a subscriber to move a
phone call between the desk phone and the mobile phone. Feature is invoked from the mobile phone.
Call Push (Mobile->Desk Call Move) - Allows a subscriber to move a
phone call between the desk phone and the mobile phone. Feature is be invoked from the mobile phone.
Class of Restriction (COR) (PBX) - Defines the restrictions that apply
when a user places or receives a call. The Accelerator supports COR for mobile originated calls.
Class of Service (COS) (PBX) - Allows or denies user access to some
system features. The Accelerator supports COS for mobile originated calls over SIP lines.
Table 2 Accelerator PBX Level 2 Integration
Feature Support Comments
Call Accounting Codes No Call Coverage/Hunt Groups Yes Call Line Identification Restriction (CLIR) (Mobile) Yes Call Pull (Desk->Mobile Call Move) No Call Push (Mobile->Desk Call Move) Yes Class of Restriction (COR) (PBX) Yes Class of Service (COS) (PBX) Yes
Accelerator PBX Level 3 Integration
Integration Level 3 provides features that are specific to the PBX or specific to vertical markets. The Accelerator does not currently support any level 3 features on the Asterisk Lines PBX.
Acronyms
Table 3 Acronyms
TERM DEFINITION Accelerator Tango Enterprise CA Certificate Authority CDR Call Detail Record CFA Call Forward All Calls CFB Call Forward Busy
CFNA Call Forward Not Answered CLI Command Line Interface CLID Calling Line Identification
CLIR Calling Line Identification Restriction COR Class of Restriction
COS Class of Service
CTI Computer Telephony Integration DID Direct Inward Dial
DN Directory Number
DTMF Dual-Tone Multi-Frequency IPDR Internet Protocol Data Record Mobilizer Tango Carrier
MWI Message Waiting Indication NAT Network Address Translation PBX Private Branch Exchange PDN Pilot Directory Number
PSTN Public Switched Telephone Network SIM Ring Simultaneous Ring
SIP Session Initiation Protocol
SMDI Simplified Message Desk Interface SOAP Simple Object Access Protocol TDM Time Division Multiplex
TLDN Temporary Location Directory Number TLS Transport Layer Security
Tango Networks, Inc. 3801 Parkwood Blvd, Suite 500 Frisco, Texas 75034 USA phone: + 1 469-229-6000 fax: + 1 469-467-9840 www.tango-networks.com