STUDY ON RECENT TRENDS AND
OPPORTUNITIES IN CLOUD
COMPUTING
V. VIJAYALAKSHMI
Assistant Professor, Department of CSE,
Christ College of Engineering &Technology, Puducherry. vivenan09@gmail.com
R. VIJAYALAKSHMI
I-Year M. Tech, Department of CSE,
Christ College of Engineering &Technology, Puducherry. viji.ramanidass@gmail.com
S. GAYATHRI
I-Year M. Tech, Department of CSE,
Christ College of Engineering &Technology, Puducherry. gayuit11@gmail.com
Abstract
The emerging trend of cloud computing that delivers the computing as a service rather than a product whereby shared resources software and information that are provided to computers and other devices as the utility over the network. Cloud computing model is composed of three service models Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS) and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and four deployment models Public, Private, Hybrid/mixed. In this paper Cloud computing system that consist of inter- connected computers and virtualized computers that are dynamically provisioned and presented as one or more unified computing resources based on service-level agreements established through negotiation between the service provider and consumers. The introduction of hardware monitoring and software management that was proved to be effective tools for managing the data centers at different locations. This paper further deal with comparative study of data centre challenges of different cloud vendors.
Keywords: Services; Dynamic Provisioning; Data centre challenges;
I. Introduction
Cloud Computing has more attention nowadays. The government agencies, enterprises, and more companies started to use Cloud Computing. The next revolution in IT and the big switch in IT is shifting the paradigm of classical computing to cloud environment. In Classical computing buying and owning the system software, hardware, application software to meet the peak needs. The system configuration, testing, verification and evaluation raise the demand of using resources. The cost of using the resource utilization is higher in order to meet the demands. In Cloud computing environment the storage of data and faster evaluation of CPU utilization and provides subscription of the data storage and pay per use of service as per the quality of services.
Cloud computing is different from other technological trends but related with grid computing, utility computing and transparent computing. Grid computing is a base form of distributed computing whereby a
storage, as a metered service similar to a traditional public utility such as electricity, water, gas and telephone services. Transparent computing is a complex back-end services that are transparent to users which is simple and easy-to use provides front-end interface.
Gartner projects the worldwide cloud revenues to reach $68.3 billion for 2010 (a 16.6 percent increase from 2009), and forecasts revenues to surpass $148 billion by 2014. Cloud computing paradigm has one glaring problem: security, Service level agreement, standardization. Since the Cloud is a new paradigm, which involves careful planning and execution [1].
The characteristics of a cloud server that includes the following:
• Ease of use-Includes simplified deployment and maintenance and portability.
• Instant availability- provides access to the server via a direct cabling that are connected over the Local Area networks and the internet.
• Subset of functionality
• Privacy in nature- we own our data and control over the data.
• Overall controlling power of software resources [4].
The rest of the paper is organized as follows. Section 2 analyzes the different service models and its architecture in cloud computing. Section 3 describes about the dynamic provisioning. Section 4 lists the challenges of data center and Virtualization techniques. Section 5 explains the comparative study on different cloud vendors. Finally the paper is concluded in section 6.
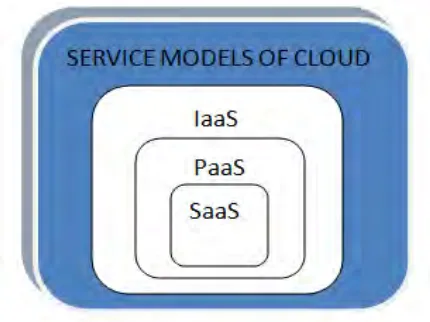
2. Service models in cloud
There are three service models that provide different aspects of services to the users of cloud environment.
• Software as a Service (SaaS) - This uses the provider’s applications over the network
• Platform as a Service (PaaS) - This provides the facility to deploy the applications to cloud
• Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) - This provides the fundamental computing resources such as rentalprocessing, storage, network capacity.
The service model architecture is as follows:
Figure 1: Service models of cloud
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Cloud computing is an evolving and trendy platform for building and running traditional web-based applications, a concept of an environment that provides known as Platform-as-a-Service. PaaS is an outer layer of the Software as a service model application delivery model. The PaaS model makes all of the facilities required to support the complete life cycle of building and delivering web applications and services entirely available from the Internet, all with no software downloads or installation for developers, IT managers, or end users [2]. For example Google App Engine, Microsoft Azure.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
As in case of software that are purchased and installed on our own personal computers, also referred to as software as a product. Software as a service is a software distribution model in which applications are hosted by a vendor or service provider and made available to customers over a network, typically the Internet. SaaS is increasingly becoming a competitive delivery model as an underlying technology that support web services and service-oriented architecture (SOA) models that makes challenging features and new developmental approaches which spreads the popularity and creates the suitable environment to customers by providing as a the service models. SaaS is also a pay-as-we-go subscription licensing model [2]. For example is SalesForce.Com uses SaaS
2.1 Architectural framework for cloud deployment models
The architectural framework for cloud bases are:
Figure 2 Deployment models of cloud
2.1.1. Public Cloud
Public cloud supports third party multi-tenant Cloud infrastructure & services. Public cloud is available on subscription basis (pay as we go for use of service).
2.1.2. Private Cloud
Private cloud runs on the company’s own data center and also used as the personal cloud management the infrastructure it leases to the users as the pay per use of service this can be used as the internal and partnership basis.
Hybrid cloud is the mixed form of public and private cloud. Supports the both cloud deploying forms that if the private cloud is insufficient capacity to use then the alternate use of the public infrastructure cloud services are provided to use by leasing agreement standards.
Benefits of cloud models are:
• No upfront infrastructure investment-No procuring hardware, setup, hosting, power.
• On demand access- service level agreement what we need and when we need.
• Efficient Resource Allocation – Global sharing environment can always kept busy by serving users from different time zones, regions, locations.
• Pricing values - Based on Usage, Quality of service, Supply and Demand, Loyalty and Standards.
• Application hastening - Parallelism for large- scale data analysis, data movement, restructuring.
• Highly Availability, Scalable, and Energy Efficient
• Supports Creation of third party services & offerings that are flawless- Builds on the infrastructure and follows analogous to the Business model as in case of Cloud infrastructure.
Figure 3. Worldwide use of cloud IT services.
The world wide spread of IT services of cloud and on demand service premises that shows the drastic change in the use of cloud services [5].
3. Dynamic Provisioning
Dynamic Provisioning Environment (DPE) is an environment that exhibits a complex networked server computing environment where server computing instance and Virtual Machines that are deployed or instantiated from the centralized administrator and client application can be accessed via server administrator, network administrator or any other users who are enabled. The server administrator or network administrator are capable to parse out control of the provisioning location to users or accounts in the network environment such as end users, organizational units, system accounts, other managerial administrators. The provisioned servers can be in or out of the firewall or hosted depends on the supporting pool of networking server which computes resources. As in case of the end user development or client who requests the server can be deployed automatically [3].
There are two provisioning management environment that are supported to use the desktop and client provisioning instances. Desktop Dynamic Provisioning Environment (Desktop DPE) or Client Dynamic Provisioning Environment is a Dynamic Provisioning Environment (DPE)is being utilized to provision client computing instances or desktop computing instances [3].
In IBM the Services that are accomplished for Cloud which offers on-Demand provisioning of virtualized server resources in a molded with security richness, private cloud atmosphere [8].
Key features of IBM Services for cloud that includes the following:
• Rapid provisioning of the service, on time delivery mode.
• Flexible model for sourcing
• Reduces risk by using the swift to minimize the cost of entry points and quickening the process to start the solutions to speed up to reach the marketplace on time delivery.
• Offers an end-to-end service strategy, deployment, integration, testing, and sales training and managerial issues.
IBM Implementation Services offers the private cloud deployment model with on- demand provisioning of dynamically scalable, virtualized server resources in a security-rich environment. This offers and creates a flexible, comprehensive private cloud environments that can be started to range from a basic installation of IBM's Integrated Service Delivery Manager (ISDM) to a sophisticated carrier-grade cloud service provider platform to opt for.
An environment is well suited for the development of the product and test on-premises IT services, and is designed to help and make a diagnosis that realizes a quick return on investment. The basic environment allows us to start transitioning our enterprise IT to a flexible new sourcing infrastructure model that helps to minimize the risk of our mission critical applications.
The major advantage to the cloud service providers are highly scalable carrier-grade cloud service management platform by positioning themselves to realize significant new revenue streams which makes a boosting up to strengthen the key enterprise customer relationships and supply of products and service level regulations.
In IBM's carrier-grade platform reduces costs for the best optimizing operations. The service platform is rational and automated; on projecting in advance the analytics that are provides the dynamic provisioning for the virtualized resources which is required to support new services, and to automatically release them when they are no longer needed as in the concept of release after use.
Major importance to support and assess IBM’s platform are as follows:
Microsoft licenses are required, including Windows Server operating system, Exchange, SharePoint, Internet Information Services (IIS), Threat Management Gateway (TMG) Server, and BlackBerry Enterprise Server are planned to be available to use the service.
IBM is a registered trademark of IBM Corporation in the United States, other countries, or both. Microsoft and Windows are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States, other countries, or both. Other company, product, and service names may be trademarks or service marks of others.
4. Challenges of Data centre
To satisfy the business needs and day to day activities of computing resources that shares resources and flexible environment which authoritatively deals with the business trends and customizes the schedule by offering the cloud service. And customers don’t need to invest the capital to use these services provided, comparatively what we have today is a reliable and cost-effective alternative to what has been using and available in the past. Customers are able to connect to the cloud by using on-demand use of sharing resources without installing software or buying specific hardware. An immense rationale for their aspiration to use the cloud is the availability of collaborative services. Collaboration is the major concern of the masses in
Dimensions of data centre: electrical power and scaling that determines total data center size: 50,000 – 200,000 servers. Servers are divided among hundreds of different services across diverse platform.
Scale-out is vital: Some services may have 10s of servers, and some might have 10’s out of 1000’s of servers [6]. Total cost variation that defines towards up of $1/4 B for mega data center Server costs dominate, Network costs are significant.
4.1 Challenges
Virtualization changes on the whole thing in today’s environment of computation. Virtualization is demonstrated to be a software technology that is rapidly transforming the IT landscape and fundamentally changing the way that people compute. The frequently used terms with different terminologies such as Operating system virtualization, server virtualization, kernel virtualization, hypervisors—virtual machine platforms, such as VMware and Microsoft Hyper-V, are typically the first and traditional form of virtualization introduced to the data centers. These technologies are flattering towards more inexpensive and less complex every day to use the service, making them attractive technologies to be the first virtual―guinea pigs in the data center.
Some of the factors that are sticky pointed as of consolidation, cost savings, dynamic provisioning, and fluid migration are motivating towards most IT shops to experiment with some of today’s form of virtual machine product, and the dawn of large-scale infrastructure systems has moved these old style of experiments and development environments into chock-full, public-facing application infrastructure systems [7].
4.1.1 Virtualization and its techniques
Virtualization is the base for cloud computing which provides the way to utilizes resources in cloud. The remote data center delivers the services in the virtualized manner. There are two techniques followed for virtualization process:
4.1.1.1 Full Virtualization
Full virtualization is the technique in which all the software can be installed in one machine and that can be run on one or more machines. It is essential for specific hardware combinations to be used. AMD-Virtualization and Intel virtualization techniques made this virtualization concept easier.
Full virtualization purposes:
• Sharing the resources among multiple users.
• Isolating user from each other.
• Emulating the hardware such as BIOS, drivers from one to another machine.
4.1.1.2 ParaVirtualization
ParaVirtualization is another technique that allows multiple operating systems that communicate in a single machine at the same time by more efficiently utilizing the system
resources such as processor and memory.
ParaVirtualization is best in some deployment as follows:
• Disaster recovery management
• Migration management
4.1.2 Deployment Challenges of virtual machine
4.1.2.1 Deficiency in Performance and Availability — The reason that resource starvation virtualization which moves many I/O tasks tuned for hardware to software via the hypervisor or server virtualization. By illustrating this particularly, if an application is optimized for a particular chipset, when the OS is virtualized then the chipset becomes a virtual software component and many of the optimization issues can be failed to survive further. The translation layer of the virtualization is now responsible to translate the optimized coed for the software chip back to the physical chip or CPU running on the underlying hardware. I/O demanding applications, like cryptographic processing applications for SSL, don’t fit to be cost healthy when virtualized due to the reason of this translation layer.
4.1.2.2 Application Awareness is lacking — Operating System’s virtualization does not solve application virtualization that leads to one of the limitations of hypervisor- and kernel-based virtualization solutions are that they only virtualizes the operating system and not even aware about the rest of the other applications that runs on the operating system. In addition to that, those same applications don’t have realization that they are using virtual hardware on top of a hypervisor. By ensuring that on inserting this extra software management layer between the application and the hardware as the mid-term service layer, the applications might encounter performance issues that are beyond their control of the application manager to control the system service.
4.1.2.3 Virtualization Features are unused — In virtual platform the batteries are not included to the new virtual platforms that are included to many advanced networking technologies, such as software switching and VLAN segmentation support. As many of these some of the features are anywhere, it is localized and isolated to the virtual machine platforms and not integrated with the rest of the network infrastructure that are as part of the virtualized system. For instance, an enterprise may have purchased VMware specifically to use for the DRS and VMotion live migration features, but then they realize that their current networking infrastructure does not support these new features, or that they have to re-architect physical portions of their network to take an advantage over the virtual software switching features. Habitually, new technologies perform flawlessly in development and trying to stage but they are unable to scale to production levels once deployed. These new platforms may have emerged with technical infeasibilities by integrating with existing applications and storage networks, by requiring a remodeled design of the data center from the traditional one in to a newly implemented in one virtualization technology.
4.1.2.4 Storage Network overflows — Managing Explosive Growth throughout by converting physical machines to virtual machines is an asset for building dynamic data centers, hard drives that becomes extremely large flat files virtual disk images—a typical Microsoft Vista Ultimate install consumes 15 gigs of local storage for the OS separately, not counting data files and other configuration files. Consequently, file storage can quickly become insurmountable. Operating system and data files that are typically reside on internal storage in physical server environments are often moved to share network storage during the virtual migration process that happens frequently. This leads to a challenging extension of existing storage as well as break growth models that may already exist for storing data on the network. On the recent analysis report from Enterprise Strategy Group, 54 percent of the customers surveyed reported some increase in storage capacity specifically tied to OS virtualization and the installation of virtual platforms.
connection.
4.1.2.6 Managerial Complexities — throughout all areas of the data center among many a single break in the pane, managing virtual machines as part of the complete management solution can resist at best moment. In case if any tools are to be used to manage the application and operating environments of each physical machine — either by using clients on the systems or by measuring application metrics on the wire such as latency time, response time, and so on — management of the virtual machines themselves doesn’t have to change our management infrastructure.
In case of Virtual machines that reports the same types of metrics as compared to physical machines. The management challenge with virtual machines appears in two forms:
1. By adding up of two new components that are needed to be managed: the hypervisor and the host system. Several among these one of these device that exists in the physical server world are not be a part of existing data center management solutions, but they do have a major contact on the performance of virtual machines from the location where it resides. On managing these devices and insight into these performance differences is critical to handle.
2. On managing our virtual machines, application network, and storage network together: Many virtual machine platforms that include high end services, built-in management tools, some of them highly sophisticated, such as VMware’s Virtual Server. When we are using these tools that provides essential management tasks, like live migration of virtual guests from one host to another; without any need to use of the external information to share with. For example, while we consider the VMware Distributed Resource Scheduling (DRS) can invoke a virtual machine live migration based on the CPU and memory constraints of the host, but it do not have a look over the internal network as part of the virtual switches nor the external network as part of the physical host port.
5. Comparison on Amazon and Rackspace
Properties Amazon ec2 Rackspace Cloud Servers
Support 24x7x365 support
24x7x365Chat/Phone/Ticket Support
Third Party Software Support
No support Supports for aLinux, Microsoft Windows Microsoft SQL Server, Apache, MySQL, .Net/IIS (Windows)
Admin Level Troubleshooting
Support will not log in to EC2 server to help its customers fix a problem.
Support to log in to a customer’s Cloud Server to help in fixing the solution to the problem.
Persistency Instances are transient or ephemeral.
Server has inherent protection against drive failures.
Server size utilization Standard Instances start at 1.7
GB. introduced Micro Instances starting of 613 MB customers.
Cloud Server sizes, starting at 256 MB and going up to 30 GB. Cloud Servers are resizable, scalable without any re-establishment.
Hybrid Hosting
It does not offer hosting on dedicated/managed servers. The computation of optimal solution support to the business
environment.
It supports for dedicated/ managed servers depending on the user needs, with a
combination of both. Helps in creating the optimal solution for computation in business aspect.
CPU Scheduling policies Instances have a capped CPU.
Micro Instances are use to add extra CPU resources.
Guarantees minimum CPU power with free bursting when extra capacity is available on the host.
Computing control and pricing benefits
The pricing of EC2 instances is lower, if it tries to takes more than once then twice the time to complete a task, the total price to complete a task increases and reduces the cost benefits.
When compared to EC2 the US- Based cloud server is more powerful and two times faster than the EC2.
Disk I/Outilization Show better performance than their built-in ephemeral storage.
Have a higher disk throughput.
IP Addresses configuration More complex.
Simple dedicated and persistent public IP address.
Philosophical issues
Amazon has less support on an open-source approach for cloud interoperability.
Distributed Management Task Force (DMTF). Develop interoperability support and standards.
6. Conclusion
References
[1] Dynamic Provisioning Environment http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dynamic_Provisioning_Environment. [2] GartnerNewsroom,http://www.gartner.com/it/p ge.jsp?id=1389313
[3] IBM Implementation Services for Cloud offers on- demand provisioning of virtualized server resources in
a security-rich, private cloud environment http://www-01.ibm.com/common/ssi/rep_ca/1/897/ENUS611-051/ENUS611-051.PDF [4] John W. Rittinghouse James F. Ransome information on cloud computing implementation, management and security, 2010. [5] Market oriented cloud computing from manjrasoft.
[6] Microsoft research on Data center challenges. http://www.nanog.org/meetings/nanog47/presentations/Tue sday/Maltz_monsoon_N47_Tues.pdf
[7] Sang-Ho Na, Jun-Young Park, Eui-Nam Huh presented the personal cloud computing security framework.